5 Phishing Mistakes Hurting You and Your Customers
Let’s take you a little back in time when you opened the email inbox. Were you outraged with the number of emails trashing both inbox and spam folders? Did you just skim over some of them to find out what was more important?
Well, that’s an average day for anyone on the planet with an active email id. And some of us, simply click on what seems important to save time and get things done quickly. That is just one of the phishing baits causing financial damages, identity thefts, and data breaches. Sounds too much?
- 156 million phishing emails are received every day.
- Out of these, 16 million actually land in the inbox, passing spam tests.
- 1 phishing attack hurts customers or businesses every minute.
While the larger notion on such attacks is that they hurt individuals more than the companies, it’s incorrect. It’s not our fault either, that is what we read, isn’t it?
The truth is that phishing attacks cost $70.2 billion to companies globally. And we haven’t even added the amount of money lost by a bad rep. After all, customers and visitors don’t care if your company was at fault or not. They just don’t want to be associated with a brand with a negative reputation. Here are some of the mistakes that can take your company to the dark route.
Phishing Mistakes Hurting
1. Not conveying what phishing attacks are and how they work.
Let’s analyze this unbiasedly here. Isn’t phishing just another fancy technology term to an average customer or website visitor? It’s one of the things we call tech jargon, and people just don’t care to understand it.
It is an organization’s responsibility to educate customers and employees so that they don’t fall prey to such attacks. Because if that happens, you are going to lose more than anyone else in the process. Banking is probably the only sector making efforts to raise awareness on the issue. While you might not want to take awareness of that level, talk about it, write posts, and send newsletters.

2. Outdated applications and operating systems.
Phishing, just like any other sophisticated attack pattern, relies on evolving. As and when new phishing detection tools are built, attackers polish phishing techniques too. That is why it is important that all the admin systems are running on updated operating systems.
Web and mobile applications should also be patched after new vulnerabilities are found and resolved. It is equally important that you run penetration testing after every update, minor or major.
3. Not reporting or spamming phishing attempts.
Engineers rely on accepted red flags to filter phishing attempts. It is more of a hit and miss method that keeps on evolving, as and when new phishing methods are developed. Unfortunately, around 16 million phishing emails escape email filters daily because tech engineers have no clue how to detect them.

As an organization or an individual, it is our responsibility to report and spam such incidents so email clients can learn from them. Such practices will improve their detection signatures and help us limit such emails. Of course, it applies to other kinds of phishing too.
4. Perceiving of phishing as immature.
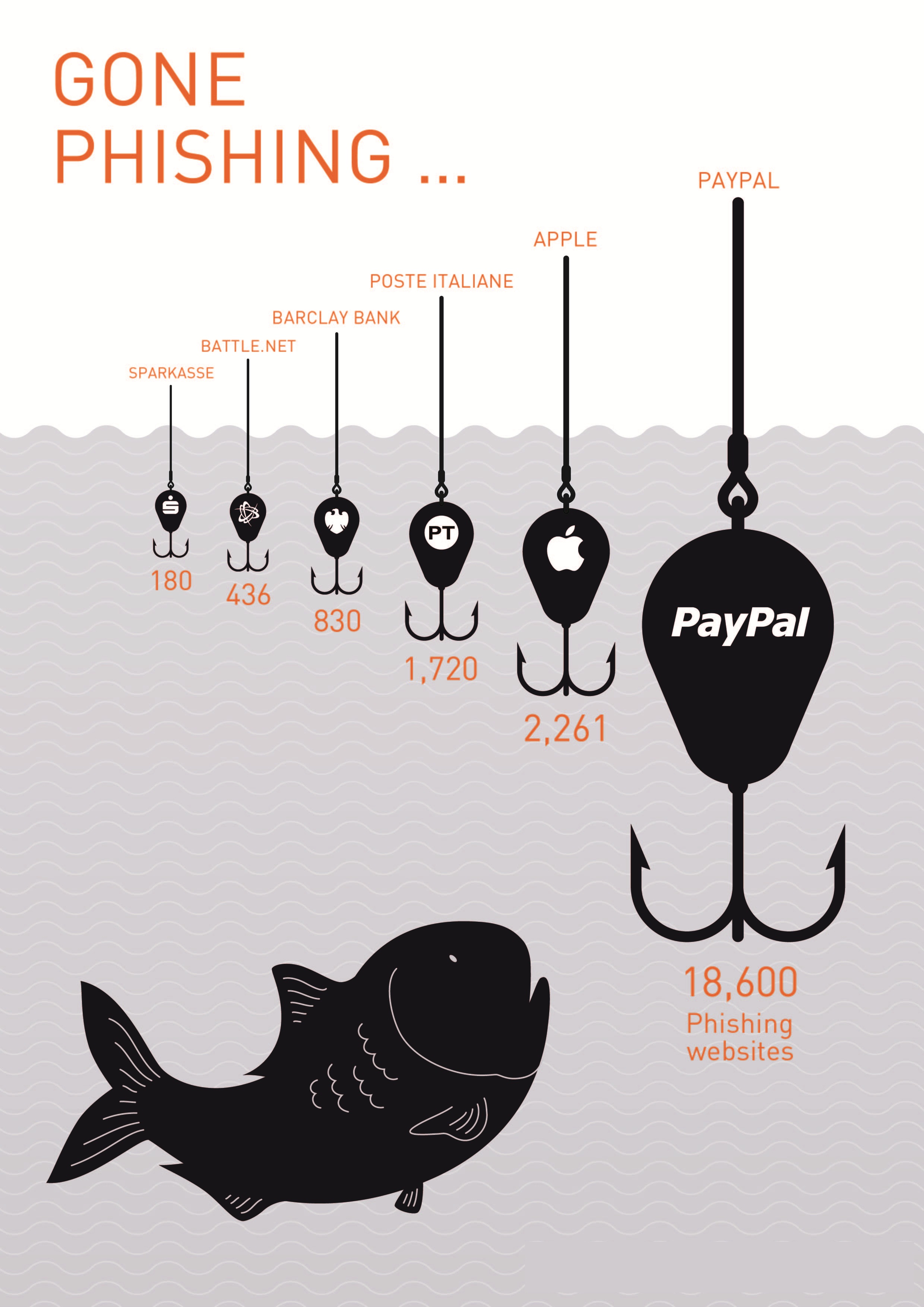
What are the ingredients of a phishing attack? A spam email, some dubious website, and collect personally identifiable information? Interestingly, most CIOs and CISOs associate phishing with deception. However, there are actually 9 other types too that have persistently troubled giants like Apple and PayPal.
Right from malware-based attacks to keylogging; there is a lot that average companies do not know of phishing. Here’s to get a brief idea of different types of phishing attacks.
5. Too many unvalidated redirects and forwards.
Have you taken care of the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities on the website? We have recently talked about how ‘A10- Unvalidated Redirects and Forwards’ vulnerability can also make it easier for hackers to perform these attacks.
Most websites don’t even know about such unauthorized redirects that look genuine. While customers should be careful about phishing, how could someone suspect that they’ll be redirected to gettingrobbed.com when it looks identical to their trusted website.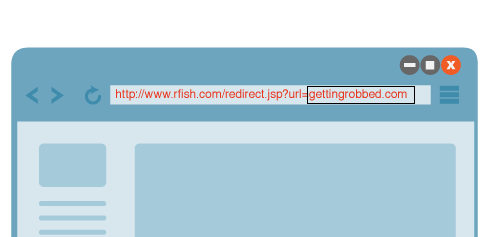
To get rid of this vulnerability, you should find out at what places it resides with the help of web application scanning. Once you have the report, make sure all the redirects and forwards are dealt with.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security updates. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn

 December 8, 2015
December 8, 2015






