Credential Coercion Vulnerabilities in Ivanti Endpoint Manager
Multiple vulnerabilities have been discovered in Ivanti Endpoint Manager, affecting various file hashing functions. These vulnerabilities—CVE-2024-10811, CVE-2024-13161, CVE-2024-13160, and CVE-2024-13159—allow credential coercion, which can lead to path traversal and potentially enable remote code execution (RCE).
Breakdown of the Vulnerabilities
CVE-2024-10811 – Credential Coercion in GetHashForFile
The GetHashForFile() function can be exploited to coerce Ivanti Endpoint Manager into authenticating against a malicious server. Since it passes user-controlled input to GetHashForSingleFile(), attackers can abuse this function for NTLM relay attacks, potentially leading to credential theft and unauthorized network access.
CVE-2024-13161: Credential Coercion in GetHashForSingleFilex
A similar vulnerability exists in GetHashForSingleFile, which also enables attackers to trigger an NTLM authentication request when a file is processed for hashing. This behavior can be exploited to capture authentication credentials, potentially leading to domain compromise. This vulnerability can also be leveraged for arbitrary file access, facilitating data exfiltration or further privilege escalation.
CVE-2024-13160: Credential Coercion in GetHashForWildcard
With GetHashForWildcard, an attacker can manipulate file paths or wildcard-based file path functions to coerce NTLM authentication requests. The risk increases if wildcard processing includes remote file paths controlled by an attacker.
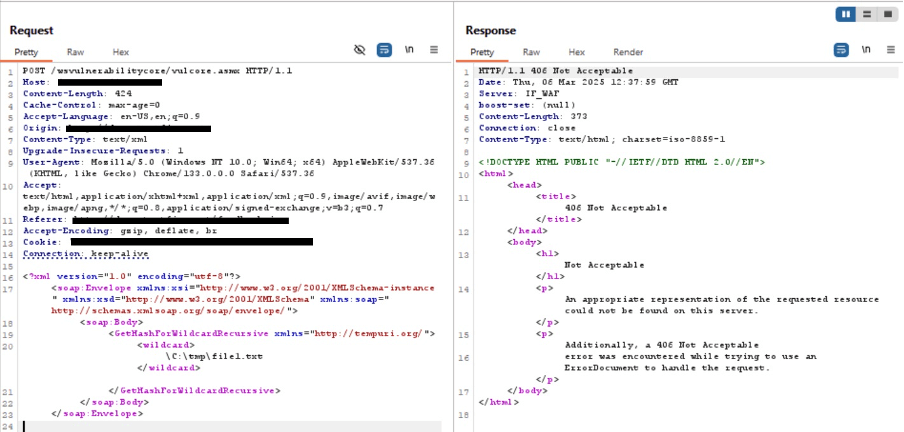
CVE-2024-13159 – Credential Coercion in GetHashForWildcardRecursive
A more severe variation of the previous vulnerability, GetHashForWildcardRecursive extends the attack surface by recursively processing files in directories. Attackers can manipulate path traversal flaws to access system-critical files and execute arbitrary commands, leading to RCE. This makes it a high-impact vulnerability requiring immediate patching.
Potential Exploitation and Risks
An attacker with network access can exploit these vulnerabilities by hosting a malicious SMB or HTTP server. When Ivanti Endpoint Manager processes a file using the affected hashing functions, it unknowingly attempts to authenticate against the attacker’s server, exposing NTLM authentication credentials. These credentials can then be relayed to other systems within the network, bypassing authentication mechanisms and gaining unauthorized access.
If successfully exploited, attackers could:
- Gain unauthorized access to sensitive internal resources
- Escalate privileges within the domain
- Compromise user accounts and perform lateral movement
- Deploy malware or ransomware in targeted environments
Mitigation and Recommended Actions
To protect against these vulnerabilities, organizations using Ivanti Endpoint Manager should:
- Apply Security Patches: Ivanti has released patches addressing these vulnerabilities. Immediate updates are strongly recommended.
- Enforce SMB Signing and NTLM Protections: Disable NTLM where possible or enforce SMB signing to prevent relay attacks.
- Monitor NTLM Authentication Requests: Implement logging and monitoring to detect unusual NTLM authentication attempts.
- Use Stronger Authentication Mechanisms: Enforce Kerberos authentication instead of NTLM where feasible.
- Restrict Outbound NTLM Traffic: Use Group Policy or security controls to prevent NTLM authentication requests from being sent outside the network.
AppTrana WAAP Coverage
With AppTrana WAAP’s out-of-the-box coverage, our customers have been protected against this CVEs from the day 0.
During PoC simulations, AppTrana WAAP effectively blocked the malicious request, as illustrated in the screenshot:
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.

 March 7, 2025
March 7, 2025






