CVE-2025-24813 – Apache Tomcat Vulnerability Under Active Exploitation
On March 17th, 2025, security researchers confirmed active exploitation of Apache Tomcat’s recently disclosed vulnerability, CVE-2025-24813. Publicly disclosed on March 10th, the earliest signs of exploitation were observed on March 12th, with attackers leveraging the flaw just 30 hours after disclosure.
This vulnerability enables Remote Code Execution (RCE) and information disclosure by exploiting Tomcat’s request-handling mechanism. The availability of Proof-of-Concept (PoC) exploit code has further accelerated attacks, making it easier for less skilled threat actors to compromise affected servers.
CVE-2025-24813 – Risk Analysis
Severity: Critical
CVSSv3.1: Base Score: 9.8 Critical
Vector: CVSS:3.1/AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H
Exploit available in public: Yes
Exploit complexity: Low
CVE-2025-24813 stems from improper input validation in specific Tomcat configurations, allowing attackers to craft malicious requests that execute arbitrary code on the underlying system. This unauthenticated RCE vulnerability takes advantage of Tomcat’s PUT and GET request handling. The vulnerability primarily impacts applications using Java Servlets, JSP, and WebSocket components, making them prime targets for exploitation.
If successfully exploited, this flaw could allow attackers to gain full control over a vulnerable system, potentially leading to data theft, unauthorized access, or server compromise.
Affected Versions
This security flaw affects the following versions of Apache Tomcat:
- Apache Tomcat 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2
- Apache Tomcat 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34
- Apache Tomcat 9.0.0-M1 to 9.0.98
How the Exploit Works
The attack follows a two-step process:
- Uploading a malicious session file
-
- The attacker initiates a PUT request embedding a Base64-encoded serialized Java payload.
- This payload is stored in Tomcat’s session storage.
- Triggering execution
- The attacker sends a GET request with a JSESSIONID cookie referencing the uploaded session file.
- This action forces Tomcat to deserialize and execute the malicious Java code, granting the attacker full control over the server.
Prerequisites for Exploitation
For an attacker to exploit this vulnerability successfully, the following conditions must be met:
To successfully exploit this vulnerability, the attacker must meet the following conditions:
- The default servlet must have write permissions enabled (disabled by default).
- Partial PUT requests must be supported (enabled by default).
- Sensitive files must be uploaded within a subdirectory of a publicly accessible upload directory.
- The attacker must be aware of the filenames of the sensitive files being uploaded.
- The upload process for sensitive files must use partial PUT requests.
Real-World Exploitation Details
- The first known attack leveraging CVE-2025-24813 was detected on March 12, 2025, in Poland.
- Shortly after disclosure, PoC exploits surfaced on GitHub, making it easier for attackers to weaponize the flaw.
Potential Impact
If successfully exploited, the vulnerability allows attackers to:
- View or modify security-sensitive files
- Inject arbitrary content into those files
- Execute arbitrary Java code remotely
- Take full control over vulnerable Tomcat servers
Official Fix and Mitigation Strategies
Patched Versions
The Apache Tomcat team has released patched versions addressing CVE-2025-24813. Users must immediately upgrade to:
- Apache Tomcat 11.0.3+
- Apache Tomcat 10.1.35+
- Apache Tomcat 9.0.99+
Workarounds for Those Unable to Upgrade
If upgrading is not immediately possible, the following mitigation steps can be taken:
- Disable writes for the default servlet by setting readonly=”true”.
- Disable support for partial PUT requests.
- Ensure security-sensitive files are not stored in a subdirectory of a public upload path.
Future Threats and Security Concerns
Researches has warned that the larger issue is Tomcat’s handling of partial PUT requests. Attackers could modify configurations, plant backdoors, or upload malicious JSP files in future attacks. This vulnerability highlights the need for continuous monitoring and rapid patching to prevent further exploitation.
Immediate Recommendations
- Update to the latest patched versions of Tomcat immediately.
- Implement strong access controls and disable unnecessary features like partial PUT requests.
- Deploy advanced security monitoring solutions that can detect multi-step exploits.
- Conduct regular vulnerability scans and penetration testing.
Why Traditional Security Solutions Fail
Traditional WAFs often fail to detect and block CVE-2025-24813 because the PUT request appears normal, without clear malicious indicators, and the payload is encoded in base64, bypassing signature-based detection.
Moreover, the attack unfolds in two stages, where the actual execution happens only during deserialization, making it difficult for conventional WAFs to recognize the threat. Since most WAFs do not inspect uploaded files or track multi-step attack sequences, organizations often realize the breach only after it appears in logs—when it is already too late.
How AppTrana WAAP Provides Out-of-the-Box Protection
AppTrana WAAP provides out-of-the-box protection against sophisticated threats like CVE-2025-24813 by leveraging deep payload inspection, real-time virtual patching, and advanced threat intelligence. It automatically decodes base64-encoded payloads to expose hidden malicious scripts, ensuring encoded attack vectors do not evade detection.
AppTrana’s managed security team continuously analyzes emerging threats and creates custom rules to provide immediate protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities—even before official patches are available. Additionally, AppTrana inspects serialized Java objects to detect ysoserial-based exploits, preventing attackers from executing arbitrary code during deserialization.
Unlike traditional WAFs, AppTrana identifies multi-stage attack patterns by analyzing and linking requests across multiple sessions, preventing remote code execution (RCE) attempts before they unfold. Its continuous monitoring of API traffic and file uploads ensures that no malicious payload slips through security defenses, blocking threats before they can be exploited. Its real-time monitoring of API requests and file uploads ensures that malicious files cannot bypass security controls.
AppTrana leverages AI-driven behavioral analysis and machine learning to detect and respond to evolving attack techniques in real-time. Its autonomous vulnerability remediation ensures that emerging threats are mitigated without manual intervention. Additionally, the platform integrates an in-built DAST scanner to continuously assess application security, proactively identifying vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. With 24/7 expert monitoring, AppTrana delivers a dynamic, self-adaptive defense system that evolves with the threat landscape, providing seamless and continuous protection.
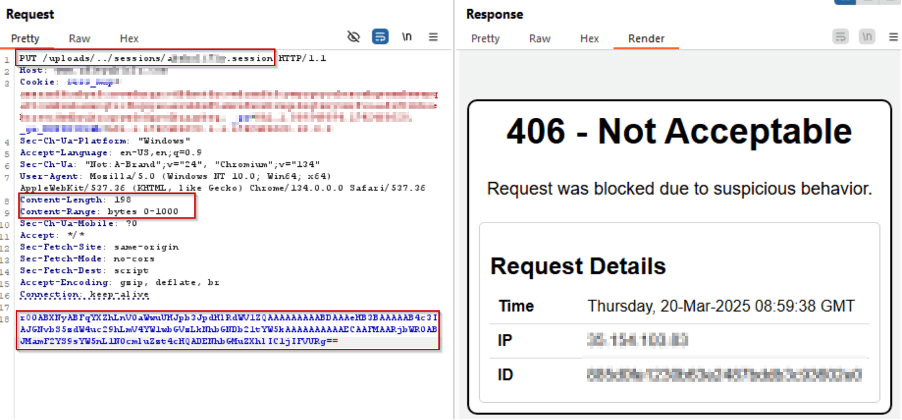
During proof-of-concept (PoC) simulations, AppTrana WAAP successfully prevented exploitation attempts against CVE-2025-24813, as shown in the screenshot.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 March 21, 2025
March 21, 2025



