Cybersecurity Lessons for 2018
The scale and sophistication of cyber attacks have kept businesses on their toes through the entire year. Large-scale data breaches such as the Equifax web server lapse combined with worldwide scares like WannaCry have reestablished what we already know- web application security is critical.
[no_toc]
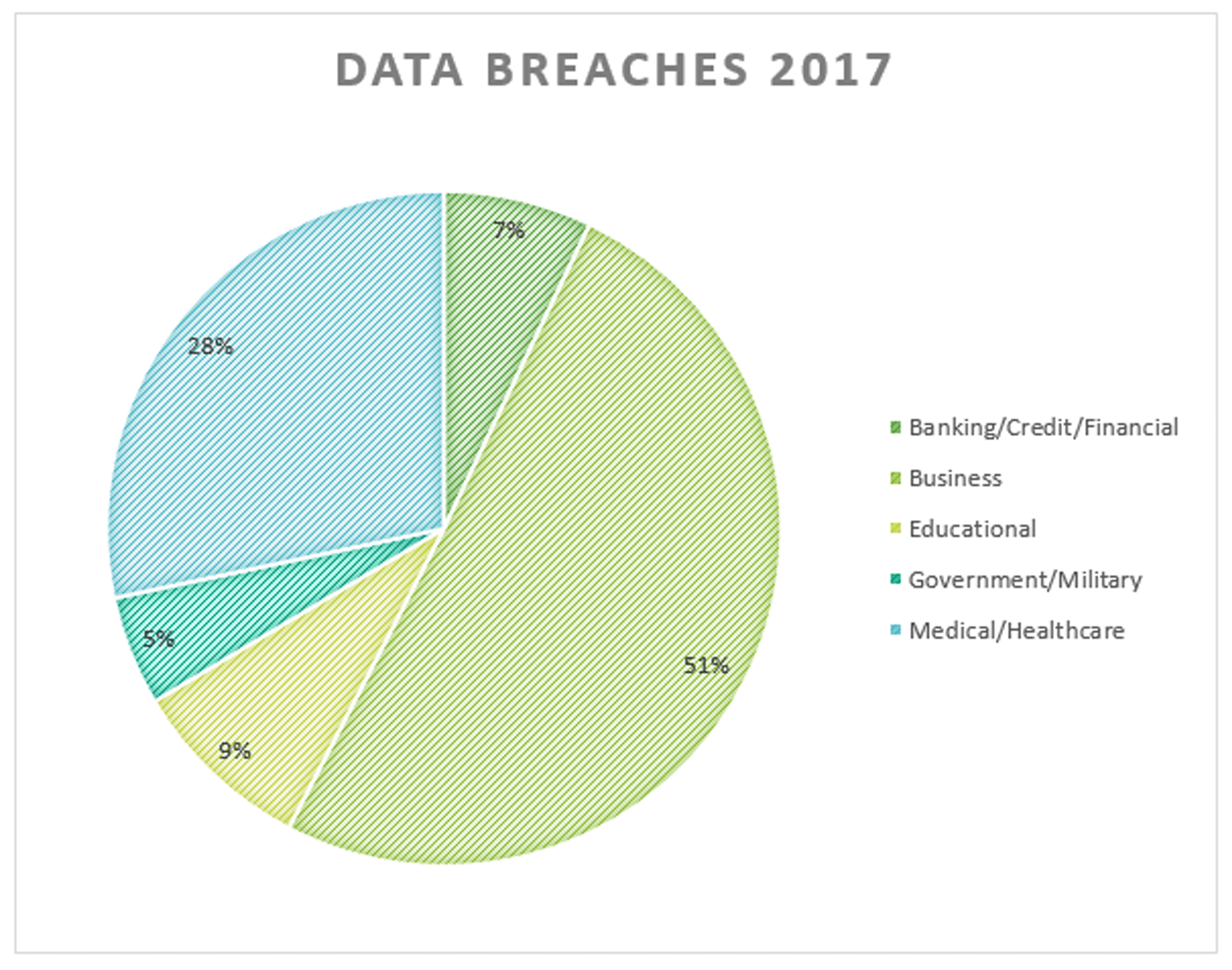
Source: Identity Theft Resource Center
Indusface, in its yearly report, is looking back at the data that we collected from over 10,000 applications. Our security analysts have put together the data and highlighted the key lessons so that the business owners can look at cybersecurity trends and prepare to deal with them in the year ahead.
Lesson 1: Bots were responsible for 90% of the attacks.
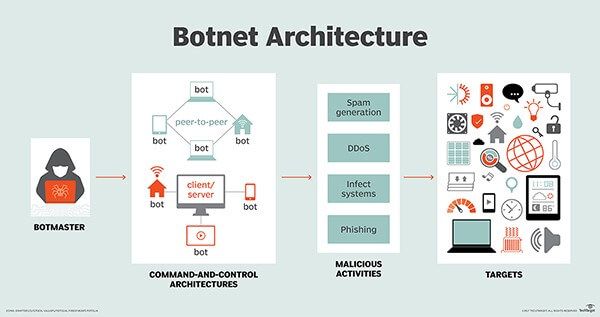
The word ‘Botnet’ is a portmanteau of ‘robot’ and ‘network’. Hackers often take control of several devices in a bid to attack web applications through spam generation, DDoS, viruses, and phishing. However, we have noticed that over the years tools like Sentry MBA have helped hackers with a list of proxies to relay the attack along with input data and inject commands into a web application.
Over one week in December 2015, cybercriminals made over 5 million login attempts at a Fortune 100 B2C website using multiple attack groups and hundreds of thousands of proxies located throughout the world.
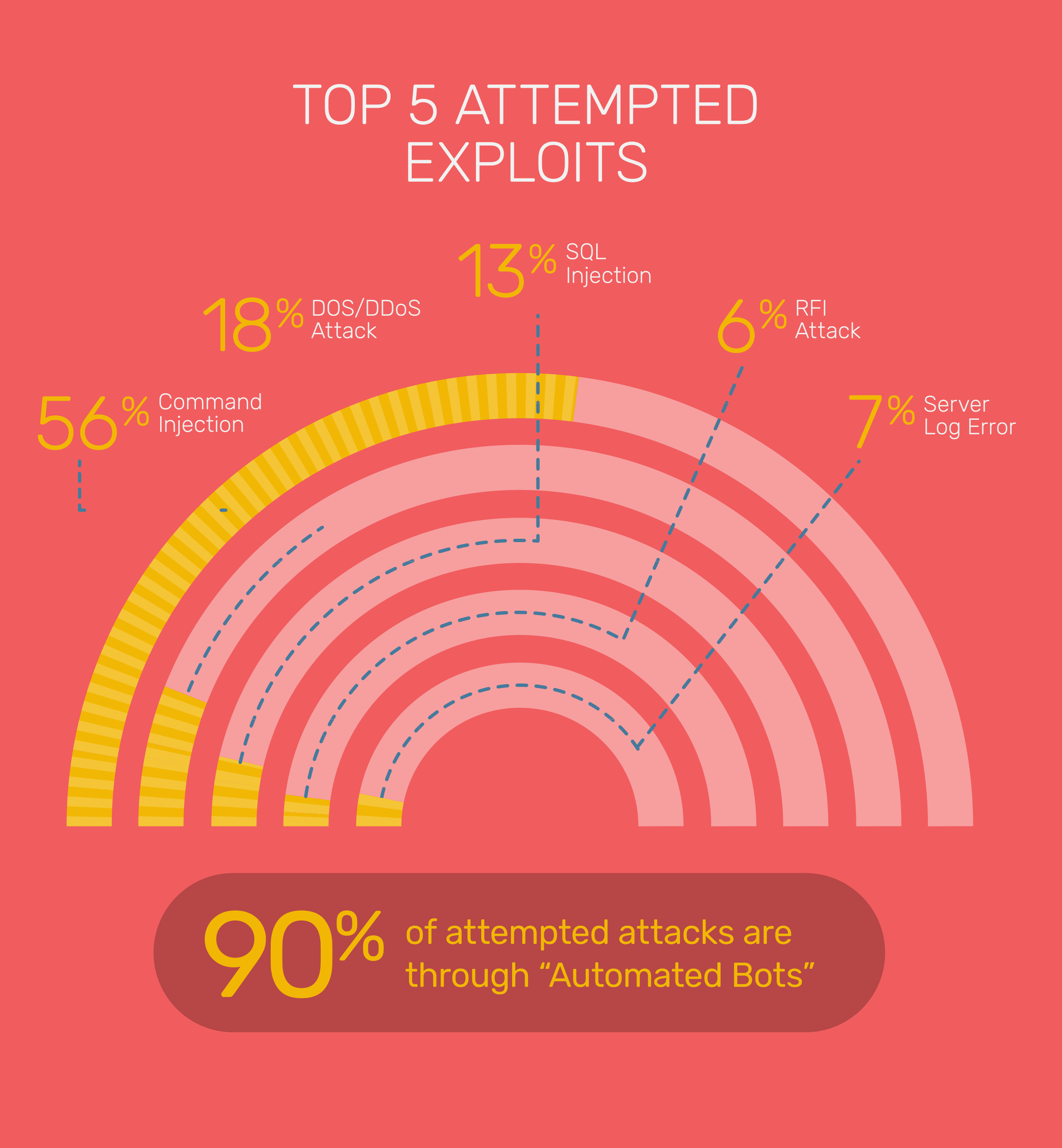
Our labs have detected an exponential rise in such attacks this year with more than half of the attacks happening via command injection and 90% of all the attacks coming from bots. It’s a clear pattern that has emerged in 2017. Hackers program bots to inject scrupulous commands. Such attacks will only rise in 2018, and protection against these is paramount.
Lesson 2: It takes more than 60 days to patch a vulnerability.
Our Signature Development team found out that out of 10,000 applications, 65 days was the average time to fix a vulnerability across all sectors. Imagine an attacker with over two months’ time to figure out breaching ways. All while the vulnerability is open to being exploited.
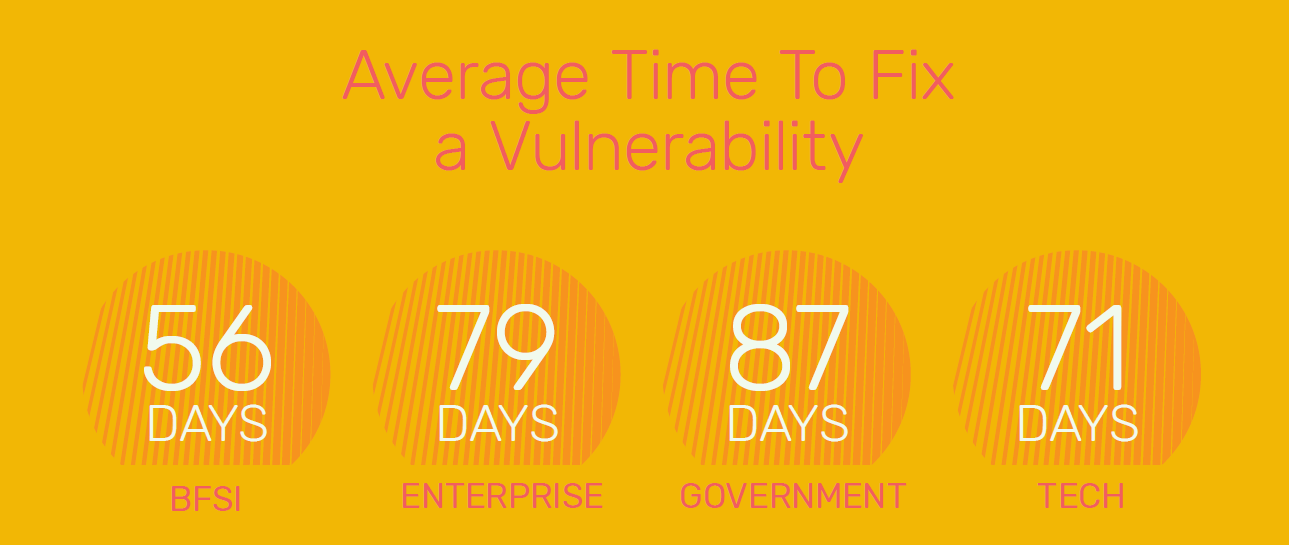
While the BFSI sector is doing marginally better, there is still a lot to cover for web applications across all sectors.
Lesson 3: Business logic vulnerabilities are on the rise, but businesses fail at finding them.
Some security loopholes are exclusive to your business. These are business logic vulnerabilities that arise due to logical flaws in the business function or flow. Since no automated tool will know about your business’ flow, they will not detect these vulnerabilities either.

New-age business applications change frequently. Calculating the security repercussions of these changes isn’t a job for tools. Ideally, it should combine frequent automated testing with manual penetration testing by security experts who understand cracking methodologies that go far beyond OWASP Top 10.
Lesson 4: CISOs look for Protection from Day 0.
Zero-Day attacks exploit undisclosed vulnerabilities that are unknown to application vendors or developers. Simply put, zero-day is a nightmare for security professionals. They cannot protect web applications until developers update the code. The vulnerability is wide open for exploit attempts, and security during the patch development period is what most new-age business CISO/CIOs look for.
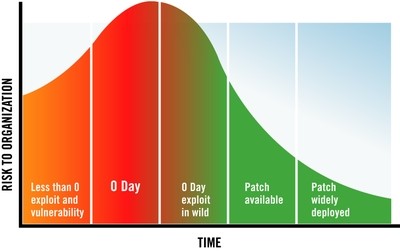
Last year, AppTrana WAF instantly protected more than 85% of vulnerabilities from Day 0. None of the 10,000+ applications that we protect had to worry about breaches from this 85% of vulnerabilities even on Day 0. For the remaining vulnerabilities, we created and deployed bespoke rules for protection.
In 2018, as more attackers use robots to look for exploitable applications after the announcement of a vulnerability, we expect CIO/CISOs and developers to look at more scalable and instant options (such as WAF) over traditional code patching.
Web Application Security 2018: The Year of Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning & Instant Protection
Efficient application security programs should rapidly detect, resolve, and prevent security threats before they spiral out of control and negatively impact your business. Attackers now have bots at their disposal to disrupt any online service in seconds. Security professionals will have to get smarter in order to identify and prevent such attempts.
- Detect Anomalies: Cybersecurity teams are tasked with adapting their technology to find new anomalies. Once machine learning and AI learn what to look for, they can quickly give their human counterparts the information they need in order to mitigate attacks and the fallout.
- Identify Advanced Attacks: Detecting and addressing advanced, complex hacks and security issues is an uphill battle. Thousands of pieces of ever-changing data and anomalies need to be quickly analyzed in order to find potential incidents.
- Quickly Respond to Attacks: In many cases, it takes more time to respond to an incident than businesses have before their systems are hit. Technology can use those lessons to stop a hack or to alert a human operator on the best practices to respond to an incident. This can dramatically shorten the response process and lessen the financial and reputation damage from a customer-facing hack.
- Lower Cybersecurity Costs: A more efficient cybersecurity process can help reduce costs and help streamline the process. Artificial intelligence and machine learning can rapidly and efficiently detect threats, resolve them, and prevent them in the shortest amount of time possible with the greatest potential for resolution.


 January 3, 2018
January 3, 2018



