Enabling TLS 1.3 Certificate – Are You Ready for Moving Forward?
Businesses are often reluctant to embrace new technologies due to assumed dependencies, perceived complications, and unclear information about the advantages. Digital communication security is not exempt from this happening and is often overlooked while maintaining an information security posture. Embracing new technologies is vital to encounter recent advancements in security, speed, and other newly available functionalities.
TLS 1.3 is one of those new technology innovations to the security and speed of secured communication. SSL/TLS certificates are the magic behind what we are simply recognized as the HTTPS, which we see in the browser’s address bar.
Here is what to know about what the latest TLS security certificate means to your business. Let’s hash it out.
What is a TLS Certificate?
TLS (Transport Layer Security), the successor of SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is a cryptographic protocol meant to offer secure communication between web servers and browsers.
Web browsers today are employing an SSL certificate that allows them to be recognized that they belong to the digitally signed CA. These certificates are TLS certificates, but most SSL certificate providers stick with the name SSL Certificates, as this is more well-known. TLS certificates authenticate one or both systems and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of information, which passes between them.
You may also want to read the difference between SSL and TLS certificates
What Does TLS 1.2 Mean?
The TLS 1.2 protocol was released in 2008 with significant enhancements over the older versions. Using secure algorithms like SHA-256 and advanced cipher suites, which support elliptic curve cryptography are few essential improvements. Up until recently, this version was considered secure, but the sighting of new vulnerabilities puts TLS 1.2’s security and reliability in question.
Possible Vulnerabilities in TLS 1.2
Researchers found the new TLS 1.2 vulnerabilities, which cause breaches similar to the old POODLE attack. The main source of this vulnerability is TLS 1.2’s outdated support of CBC (Cipher Block Chaining), which allowed MITM (Man-in-the-middle) attacks on encrypted VPN and Web Sessions. The outdated crypto method also opened the door for the GOLDENDOODLE attack, a similar yet more powerful attack than POODLE with rapid hacking abilities.
In addition to the security vulnerabilities, the privacy and performance issues were also noted in the TLS 1.2 certificate.
What Does TLS 1.3 Mean and Is It Safe?
TLS 1.3 protocol aims to address all the drawbacks of TLS 1.2. with a completely new security design, it abandons backward compatibility and removes all the vulnerable parts of the TLS 1.2 version. There is support for stronger ciphers, which are essential to implement PFS (Perfect Forward Secrecy). Moreover, it is relatively simple to implement TLS 1.3.
Among several technical differences, this version provides 3 main upgrades, which are quite vital to a normal user. These benefits are
- Better Security
- Increased Speed
- Simplified Cipher Suites
TLS 1.3 Vs TLS 1.2 – The Enhancements That TLS 1.3 Brings
1. Increased Speed with Faster TLS Handshake
Latency is the biggest factor in page load time. While encrypted communication is important to the modern web, TLS encryption requires CPU time and adds latency, which degrades performance.
Page load time matters to retain visitors, even a few milliseconds can make the difference. Fortunately, the TLS 1.3 version adds less latency than TLS 1.2, switching to the latest version will have a great head start for businesses.
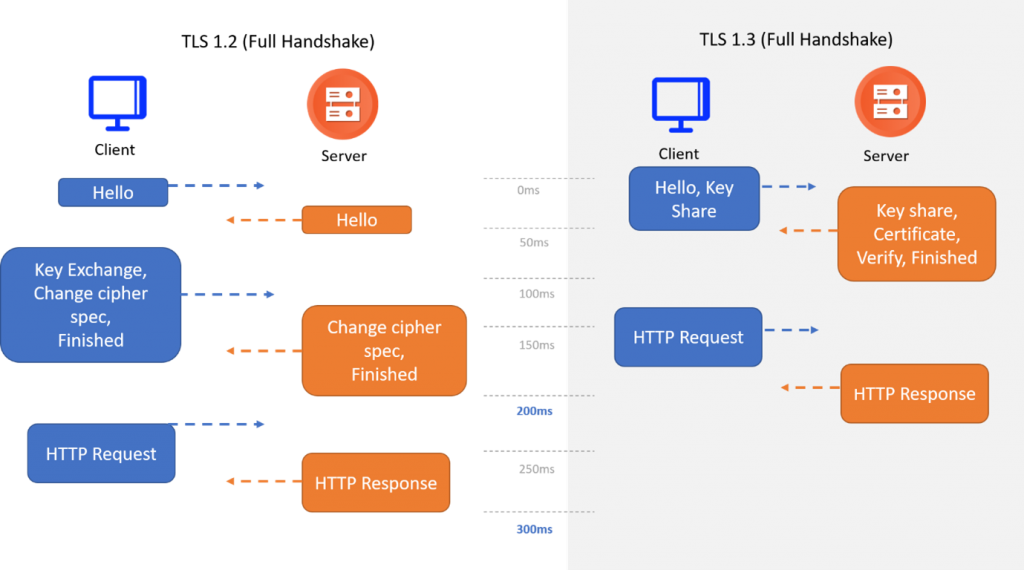
The TLS 1.2 handshake process, where the clear data needs to be encrypted as well as decrypted, typically exchanges 5 to 7 packets between the client and server to initiate a communication. It will add considerable overhead in the connection.
Under the TLS 1.3 certificate, the encryption was embraced by default, the handshake process can be completed in 0-3 packets. As the number of negotiations has now been reduced and the key exchanges and digital signature scheme no longer required in negotiation, the encryption latency and overhead are reduced, ensuring more responsive connections.
2. Zero Round Trip Time (0-RTT)
Another performance benefit of TLS 1.3 over TLS 1.2 certificate. When a user returns to an already visited TLS-secured website, it will load faster since the browser will remember that the website is trustworthy by leveraging PSK (pre-shared keys). This feature is called, “Zero Round Trip Time.
3. Privacy Benefits
TLS 1.3 enables the cryptographic technique, PFS (Perfect Forward Secrecy) by default, which adds a layer of confidentiality to the encrypted session. With PFS, this version ensures only the sender and receiver can decrypt the traffic. Even if an intruder recorded an encrypted session and gained access to the server’s private key, he couldn’t decrypt the session.
4. Simpler and Stronger Cipher
In TLS version 1.2, the use of ciphers along with cryptographic weakness has caused potential security vulnerabilities. The recent TLS security certificate supports only algorithms, which have no known vulnerabilities. TLS 1.3 also removes the renegotiation. The elimination of half of the negotiation during the handshake process results in a decrease in the cipher size too.
The earlier version of TLS security certificate uses cipher suites that include 4 ciphers as shown below:
![]()
The TLS 1.3 supports cipher suites, which don’t have key exchange & signature algorithms:

5. Makes the Internet Safer
Internet security is vital for every business. Hackers target websites, which store sensitive details about users on their servers, and high-profile attacks can ruin a company’s reputation. TLS 1.3 addresses the security issues, which plagued TLS 1.2 certificate; hence, the business, which upgrades to TLS 1.3 certificate can offer better protection.
TLS 1.3 eliminates server out-of-date and vulnerable features from TLS certificate 1.2. Here are some of the algorithms and ciphers removed by TLS 1.3:
- EXPORT-strength ciphers
- CBC (Block) Mode Ciphers
- RSA Key Transport
- DES
- 3DES
- MD5 Algorithm
- SHA-1 Hash Function
- RC4 Stream Cipher
- Various Diffie-Hellman groups
Eliminating the ciphers which don’t support PFS ensures easier implementation and at the same time closes the window of opportunity for hackers.
The Way Forward
The benefits of this latest TLS security certificate are clear. The TLS 1.3 certificate is more secure, lighter, and faster. Switching to the latest TLS certificate ensures your websites and web apps are going to be secure and faster than ever.
You can purchase the SSL certificate from the reputed certificate providers like Indusface. Being a partner of Entrust Certificate Authority, we eliminate vulnerabilities and malware, bringing an additional level of security for your business.
No matter how complicated your encryption requirements are, we aid you to keep your network and web applications more secure. Our team has proven experience and performance to meet the increasing security needs of today’s digital landscape.


 January 22, 2021
January 22, 2021


