Are You Secure Against These Recently-Found Threats?
Exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities has always been the primary choice for hackers. It is just obvious that they will be looking for new weaknesses within the layers and misuse them before anyone knows about it.
Take the Factoring Attack on RSA-EXPORT Keys of FREAK for instance. This Secure Sockets Layer vulnerability was discovered this year in March but were surprisingly present from the early 90s. It posed a man-in-the-middle threat to around 33% of all the websites and servers along with major browsers.
Undeniably, such zero-day threats are serious for the simple factor that no one knows about the exact problems. However, knowledge of such vulnerabilities resides with only the top ranks of underworld hacking pools. An average cyber crook is usually unaware, but the problems get graver when this vulnerability and their exploitation guides come online and companies fail to install patches or Web Application Firewalls with custom rules for such vulnerabilities.
CVE-2015-0235-GetHOST Vulnerability
Several Linux operating systems including Debian, Cent OS 6 & 7, and Ubuntu 10.04 & 12.04 were found to be vulnerable to what was termed as the GHOST vulnerability earlier this year. It was found that attackers could actually exploit glibc’s GetHOST functions buffering overflow in glibc function __nss_hostname_digits_dots(). When applications and DNS resolver are connected, an attacker can get IP address from the hostname and assume complete control over 32-bit and 64-bit servers.
Now a day after the GHOST vulnerability was found, most operation systems released their patches to update glibc version. In fact, our web application scanning Indusface was also updated to detect GHOST.
However, the major problem is that detailed exploitation information on GHOST is available on many forums and many companies have still not patched their OS. Surprisingly, with lack of information, many do not even know about the vulnerability for about five months now.
Also Read: All You Need To Know About Ghost Vulnerability
CVE-2015-0204 Factoring Attack on RSA-EXPORT Keys Vulnerability
A month approximately after GHOST, the ‘FREAK’ scare threatened our confidence once again on encryption technology. Though FREAK wasn’t as severe as POODLE, an informed attacker could still gain access to sensitive information and inject commands.
FREAK is believed to be a security loophole from the 90s that posed a threat to many SSL clients including OpenSSL, which is widely used to encrypt browser to server communication. Giants like Google, Apples, and Windows had confirmed in March 2015 that their then-latest operating system versions were susceptible to man-in-the-middle attacks using FREAK vulnerability.

About three months have passed since FREAK was discovered and patched, still many users have still not updated their operating systems and browsers.
Additionally, with detailed information on FREAK available online, companies also need to secure their end with vulnerability scanning and a Web Application Firewall in place to stop such attacks.
CVE-2015-4000 Logjam Vulnerability
Bearing similarities to FREAK, the recently found Logjam vulnerability made Transport Layer Security (TLS) and Secure Shell (SSH) vulnerable to a man-in-the-middle attack. It had been estimated that more than 1 million domains were at risk.
Logjam basically helped hackers downgrade the encryption to 512-bit export-grade cryptograph and decrypt it. Export-grade cipher suites were believed to be the cause of this vulnerability, so if users and companies would have dealt with FREAK properly, it should not have caused problems.
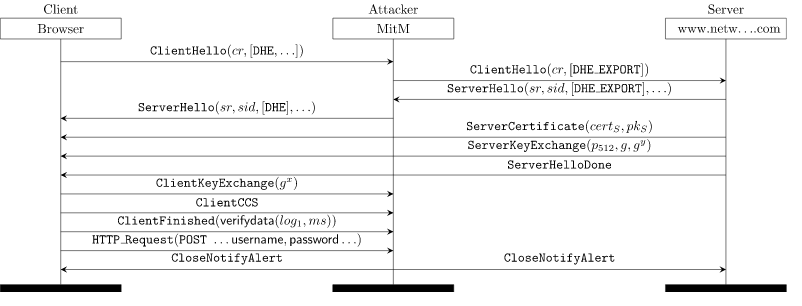
Individual users should ideally update their browsers while website administrators can use this link to enter the hostname and find if it’s vulnerable to Logjam attack. Our web application scanning and web application firewall is recommended for advanced security.
Conclusion
The exploitation of recent vulnerabilities is a major threat to organizations that do not really get security updates on a regular basis. It is critical that security professionals get aware of recent breaches, hacking attempts, and vulnerabilities in an attempt to patch their systems and servers. Alternatively, they can hire security vendors that can provide continuous vulnerability detection and protection.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 June 18, 2015
June 18, 2015



