How Virtual Patching is Helpful in Vulnerability Management
The average time to fix high-severity application security vulnerabilities grew from 197 days to 246 days just in 2021 – according to the AppSec Stats Flash report.
Most often, strong intent to fix these vulnerabilities is not enough.
Lack of access to code with third-party dependency, developer availability, and/or lack of time are some reasons why patching is practically impossible.
Also, a Ponemon study found that 42% of data breach victims agreed that they were breached due to unpatched vulnerabilities. Many of us are aware that patching is not always that simple.
Are you losing the race to patch known vulnerabilities? Virtual Patching comes as a lifesaver for your web app security.
What is Virtual Patching?
Virtual patching is a process of addressing security flaws immediately to shield from being exploited and fixing the code later. Like the software patch provided by a vendor, deep security virtual patching protects against a certain exploit.
However, the main difference, in this case, is the patching is deployed at the network level rather than on the machine itself. Virtual patching is something called proximity control because it blocks a threat before it exploits its intended target.
It serves as an emergency security tool that organizations can use to instantly address vulnerabilities on affected endpoints and servers.
In this short video clip, our Founder Venky and CTO Sunil share their expert views on virtual patching and its significance in modern cybersecurity.
Click here to listen in the full podcast , A Sub-Domain Takeover Story, Two Questions for Every WAF Provider .
What Happens to Unpatched Websites?
Unpatched vulnerabilities were key culprits in two-thirds of data breaches. The Department of Homeland Security estimates the figure to be much higher at 85%. 56% of vulnerabilities identified in 2021 are exploited even now for ransomware attacks. This makes unpatched flaws a very dangerous threat.
Patches secure vulnerabilities, flaws, and security weaknesses in websites. Permanent patches fix a vulnerability permanently. Virtual patches provide a layer of security enforcement until developers fix flaws. This ensures attackers don’t have entry points to exploit and orchestrate attacks.
Even if a vulnerability is not a critical risk, it might be the point of an exploit for attackers. Frequent vulnerability detection and control over incoming and external traffic is core to enhance malware resilience.
Cybercriminals are in a constant sprint to exploit discovered vulnerabilities before enterprises have a chance to defend. FireEye Mandiant Threat Intelligence Research suggests that most of the vulnerability exploitation happens before the issuance of the patch or within few days of the patch was issued.
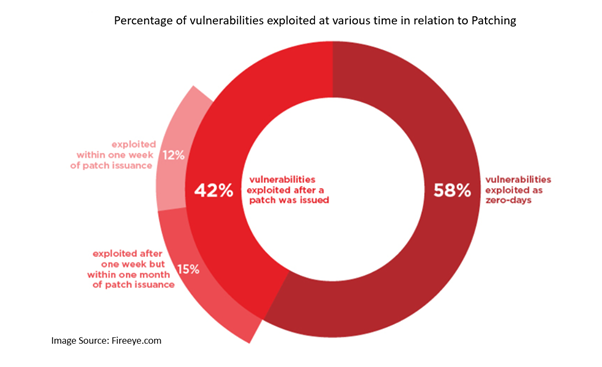
The speed with which hackers exploit vulnerabilities highlights the necessity of patching as fast as possible. However, delay in patching means the enterprise is at risk of attacks, and the cybercriminals obtain all the details they need to exploit, which entails the following issues:
- Security measure compromise
- Critical Data Exposure
- Network and System Compromise
- Reputational Loss
- Financial Loss
Patching a vulnerable system can take days, weeks, or even months, especially if there is an issue that patching might affect the app’s core functionalities.
There are some challenges which make patching even longer:
- Cost Reduction – IT team may delay software patching as it could demand costly upgrade or replacement of the legacy system or re-building of enterprise application.
- Official Patch Deployment – When patching is not made available by the software vendor, patching may be delayed
- Uptime Preservation – IT team may pause to patch as it could require keeping the business-critical servers offline
Virtual Patching: An Effective Approach to Addressing Security Vulnerabilities
Virtual patching involves implementing a layer of security policy, which prevents and intercept the exploitation of vulnerabilities. An effective virtual patching solution includes capabilities to inspect and block malevolent activity from web traffic, detect & prevent intrusions, prevent attacks on web applications, and adaptably deploy on the cloud, or physical environments.
Virtual patching solutions give security administrators a chance to review, test as well as schedule official software patches without leaving the critical system at risk.
Unlike traditional patching, it enables a flaw to be fixed without touching its libraries, the OS, or even the device it is running on. It focuses on fixing an issue by changing or eliminating dangerous behavior by taking control of the inputs and outputs of web applications. They target traffic endeavoring that utilize a known vulnerability and actively interrupt and block the traffic before it exploits the target system.
Deep security virtual patching gives you the option to protect the apps without patching them. The virtual patching solutions are faster, doesn’t require application language programming, and controls the patch cycle without compromising security. All these happen without having to keep the production servers down, which means your business can stay up and running.
Circumstances where virtual patching solutions are critical
- Virtual patching offers a short-term stop-gap solution for a critical level of coverage until a permanent patch is available
- Before deploying a permanent patch, it should be validated to check whether the patch will trigger new issues. This validation phase introduces additional delays. Deep security virtual patching is critical at this initial warm phase to shield the known vulnerabilities from exploitations.
- Virtual patching is even more important for assets, which require considerable planning as well as downtime for a permanent patch to be deployed. These assets include pipeline monitoring systems, and machines running critical systems, which play a crucial role in critical infrastructures like a hydroelectric dam or electrical grids, which can’t be taken down.
How Can Businesses Benefit from Virtual Patching?
Here’s how virtual patching solutions augment an enterprise’s existing cybersecurity management technology and vulnerability management policies:
1. Minimizes Security Risks
Vulnerability shielding is an AppSec lifesaver because it helps minimize security risks significantly. How so? The gap between vulnerability identification and its patching, called the window of exposure, directly impacts the level of risk. The larger the window of exposure, the higher the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches.
The average time taken to patch a vulnerability is currently 60-150 days and leaving the vulnerability as-is for this time period is very risky. Further, with zero-day vulnerabilities, attackers need as little as 5 minutes to get a human to click a social engineering scam. When instant virtual patches are applied, you instantly minimize your risk of exposure.
2. Buys Additional Time for Developers
Given the time developers need to develop, test, and implement a permanent patch for the vulnerability, vulnerability shielding is a big lifesaver. It extends the additional time for developers to deploy an adequately tested patch instead of a haphazard one.
3. Serves as an Additional Layer of Security
Applications have several third-party components and software that cannot be internally patched. There are also components in the IT infrastructure for which patches are no longer issued, but the component cannot be removed from the application without widespread disruption and costs. In such cases, virtual patching offers an additional layer of security and keeps these components protected.
4. Growing Number of Vulnerabilities
The number of vulnerabilities is growing exponentially, and patching them is nearly impossible from a cost, time, and resource perspective. With vulnerability shielding, you can focus on critical and high-risk ones first and leave the bulk of low-risk vulnerabilities virtually patched.
5. Prevents Unnecessary Downtimes
Developers have the freedom and flexibility to stick to their patch cycles and prevent unnecessary downtimes, crashes, and poor website performance permeating from frequent, haphazard patching processes. It also reduces the time and money spent on emergency/ ad hoc patching.
6. Infuses Scalability
It infuses scalability into the patch management process as virtual patches need not be applied across all hosts but in fewer locations. The best virtual patching solutions use intelligent automation and can deploy virtual patches instantly, regardless of the number of vulnerabilities to be secure.
7. Enables Adherence to Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory frameworks require organizations to maintain timeliness in vulnerability management, and virtual patching helps with that.
Virtual Patching Tools
There are different ways in which virtual patches are implemented – WAF virtual patching, solutions implemented with the Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), as a web plugin, and so on.
The best method has been WAF virtual patching, wherein virtual patches are administered by a comprehensive, intelligent, managed next-gen WAF like AppTrana.
Such Web application firewall virtual patching solutions offer:
- Multi-layered security that includes granular traffic monitoring and behavioral analysis to prevent threats in real-time
- End-to-end visibility into the IT infrastructure
- Instant patch any identified vulnerabilities until developers fix them
Further, AppTrana offers intelligently automated and quick, scalable, and accurate solutions – no vulnerability will be left unsecured. It can be easily deployed in cloud-based, physical, and virtual environments. It also continuously tests and scans applications to ensure the effectiveness of virtual patches.
The Closure
Undeniably, virtual patching is a valuable technique to obtain immediate protection against known vulnerabilities. To benefit from the virtual patching solutions, be conscious of public vulnerability disclosure, and perform your source code reviews and web application scanning for vulnerability assessments.
Of course, virtual patching is an invaluable technique to respond to an event immediately, however, it is not an alternative technique to permanent patching. Virtual patching can only ensure reliable protection in the interim; you still need to deploy permanent patching whenever possible.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 February 27, 2023
February 27, 2023



