227 Key Cybersecurity Statistics: Vulnerabilities, Exploits, and Their Impact for 2026
Cybersecurity Vulnerability Trends 2026
The steady increase in cybersecurity vulnerabilities over the years presents growing challenges for organizations striving to secure their digital assets.
1. One of the clearest indicators of the expanding threat landscape is the sheer growth in vulnerability reporting. Daily CVE disclosures jumped from 115/day (2024) to 44/day (2025)[Github] Expect these numbers to rise further in 2026.
2. Daily disclosures increased from 113 per day in 2024 to 131 per day in 2025, showing how rapidly new weaknesses continue to emerge.(Deepstrike)
3. The CVE database now holds over 305,000 recorded vulnerabilities, underscoring how vast and fast-moving today’s global exposure surface has become. [CVE]
4. Global vulnerability disclosures are expected to reach 31,000–34,000 CVEs in 2026, marking the highest yearly count ever recorded and reflecting a 21% YoY surge driven by cloud, API, and software supply chain complexity.[Comparecheapssl]
5. High-severity vulnerabilities also continue to climb, with 13,500–15,000 CVSS 7+ vulnerabilities projected in 2026, placing unprecedented pressure on security and IT operations teams. [Comparecheapssl]
6. Vulnerability-based attacks surged by 124% in Q3 2024 compared to the same period in 2023. This increase is largely attributed to the growing accessibility of LLM tools like ChatGPT. [Indusface]
7. With 25% of breaches linked to stolen credentials and application vulnerabilities, the importance of securing applications becomes increasingly critical in a digital-first world.[Verizon]
8. More than 99% of technologists acknowledge that production applications contain at least four vulnerabilities. [Contrast Security]
The Weaponization of Vulnerabilities
Attackers are weaponizing vulnerabilities faster than ever, making real-time defences essential for 2025.
9. Attackers now weaponize vulnerabilities almost instantly, with 33% of critical vulnerabilities exploited within the first 24 hours and many targeted within just a few hours of public disclosure. [Comparecheapssl]
10. Within the first week of a CVE release, over 54% of critical vulnerabilities face active exploitation, widening the risk window for organizations with slow patch cycles. [Comparecheapssl]
11. TheReact2Shell vulnerability (CVE-2025-55182) was weaponized almost immediately, with state-linked threat groups launching exploitation attempts within hours of its public disclosure, making it one of the fastest-exploited CVEs of 2025.
12. CVE-2025-8088, a high-impact WinRAR path-traversal vulnerability, was also exploited shortly after disclosure, demonstrating how quickly attackers move against widely deployed consumer and enterprise software.
13. In 2024, 0.91% of all CVEs (204 out of 22,254) were weaponized, representing a 10% year-over-year increase. This trend emphasizes the need for faster cybersecurity breach detection and response. [SC Magazine]
14. Browser exploits ranked second, accounting for nearly 12% of attacks, while Google’s Android was exploited in about 6% of the detected incidents during this period. [Statista]
15. In 2023, 38% of intrusions began with attackers exploiting vulnerabilities, marking a 6% increase compared to the previous year. [Darkreading]
A Surge in Identified Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Zero-day vulnerabilities remain among the most dangerous cybersecurity threats, and their prevalence has seen a sharp rise. These cybersecurity statistics highlight the increasing risk they pose to organizations and the importance of swift response mechanisms.
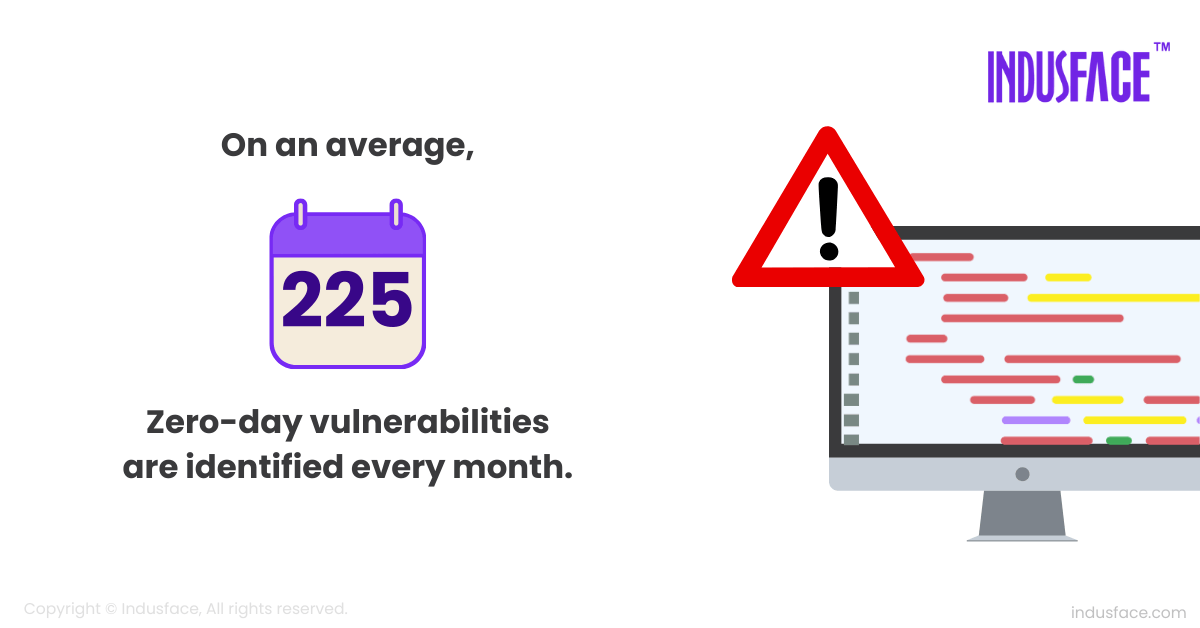
16. Detection in 2025:Between January and October 2025, AppTrana uncovered 5,755 emerging vulnerabilities, averaging 575 detections each month. This accelerating trend reflects how quickly attackers innovate and why proactive, always-on defense is essential. [Indusface]
17. Rising Numbers in 2024: In 2024, AppTrana WAAP identified 3,508 zero-day vulnerabilities, a sharp increase from the 3,324 discovered in 2023. This rise combined with over 7 billion attacks blocked across websites and APIs highlights how aggressively attackers are probing modern applications, especially APIs.[Indusface]
18. 32% of exploited vulnerabilities in the first half of 2025 were exploited as zero-day or “1-day” vulnerabilities, meaning attackers moved before patches were available or widely applied.[Vulncheck]
19. Prolonged Exploitation Windows: Attackers continue exploiting vulnerabilities long after patches exist. A clear example is CVE-2017-12637, a SAP NetWeaver vulnerability patched in 2017 but actively exploited again in March 2025, according to CISA. This highlights how delayed patching leaves organizations exposed for years, extending the exploitation window for attackers.
Impact of Unpatched Vulnerabilities in 2025
Unpatched vulnerabilities remain a top target for cyberattacks, with 2025 cyber-threat stats and past trends showing a sharp rise in attack rates. Delayed patching and poor vulnerability management significantly increase these risks.

1. The 2025 DBIRreport found that vulnerability exploitation was the initial access method in 20% of breaches, based on an analysis of 12,195 confirmed incidents.
2. Vulnerability-based attacks jumped nearly 10× as threat actors increasingly targeted unpatched flaws and insecure application features across the insurance industry.[Indusface]
3. 33% of critical and high vulnerabilities remained unpatched for over 180 days, highlighting patching challenges.[Indusface]
4. Unpatched vulnerabilities continue to be the biggest driver of breaches, with 54% of ransomware incidents in 2026 traced back to outdated or poorly patched systems.[Comparecheapssl]
5. Attackers increasingly rely on public exploit kits rather than sophisticated attacks, with nearly 75% of breaches involving vulnerabilities that already had publicly available exploits.[Comparecheapssl]
6. Across protected applications, 18,000 critical and high-severity vulnerabilities were identified. 33% of critical and high vulnerabilities remained unpatched for over 180 days, highlighting patching challenges.[Indusface]
7. Website vulnerability attacks grew from 36B → 1.71B (26% increase), showing sustained focus on legacy applications.[Indusface]
8. Across AppTrana-protected applications in India, vulnerability-based attacks surged sharply across industries, with Manufacturing experiencing a 459% increase, Retail recording a 127% rise, and the BFS sector reporting that 77% of all attacks specifically targeted application vulnerabilities. [Indusface]
9. More than 52% of enterprises fail to patch critical vulnerabilities within 30 days, causing long-term security gaps across core business systems. [Comparecheapssl]
10. A cybersecurity statistics show that 56% of older vulnerabilities continue to be actively exploited, demonstrating the enduring threat of unpatched vulnerabilities. [businesswire]
11. Exploitation Rates on the Rise:In 2024, 14% of breaches began with vulnerability exploitation as the initial access method, nearly three times higher than last year. [Verizon]
12. In mid-2025, threat actors exploited an unpatched zero-day in Oracle E-Business Suite to steal data and move laterally across enterprise networks. The vulnerability was targeted before a patch was even available, proving how quickly attackers scan for and weaponize newly exposed enterprise vulnerabilities.
13. The 2023 MOVEit breach remains an example of how quickly attackers exploit an open vulnerability: a file-transfer vulnerability was rapidly weaponized to compromise multiple industries. Its fallout demonstrated that any unpatched internet-facing vulnerability becomes an immediate, high-value target.
14. Delayed Detection:According to cybersecurity breach statistics, it took 204 days on average to discover a breach in 2024, with an additional 73 days required for containment. These delays significantly increase the risk, as shown in data security breaches statistics 2024.[IBM]
15. AI-Driven Detection:Organizations using AI-powered security systems in 2024 were able to detect and contain breaches 108 days faster, saving an average of $1.76 million per breach.[IBM]
16. Because API vulnerability attack attempts surged 13×, any unpatched API vulnerability becomes a high-probability breach vector.[Indusface]
17. Faster Containment Saves Millions:Companies that contained breaches in under 200 days saved over $1 million compared to those taking longer, reinforcing the value of rapid response, as supported by security breach statistics.[IBM]
18. Virtual Patch Effectiveness: Virtual patchesblocked 62% of web attacks and 71% of API attacks in 2024, offering a crucial layer of defence.[Indusface]
19. WAAP Integration Reduces Patching Time:Integration of vulnerability scanners with WAAP solutions reduced patch remediation times from months to just 3 days, accelerating response times.[Indusface]
Top CVEs 2025
High-severity vulnerabilities in popular software platforms have exposed significant cybersecurity risks in 2025. Ongoing exploitation of these flaws heightens the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches, underscoring the urgent need for timely patches.
20. Apache SkyWalking (CVE-2025-54057)
CVE-2025-54057 is a stored XSS vulnerability in the Apache SkyWalking web interface that allows attackers to inject malicious scripts into data rendered on dashboards. When administrators view the affected pages, the payload executes automatically, enabling session hijacking, data theft, or UI manipulation. All versions up to 10.2.0 are affected, with a fix available in 10.3.0.
21. Apache Tika XXE Vulnerability (CVE-2025-66516)
CVE-2025-66516 is a critical XXE (XML External Entity) vulnerability in Apache Tika that allows attackers to access sensitive files and internal resources by processing maliciously crafted documents. The flaw exposes Tika deployments to unauthorized file reads and potential data exfiltration. Given Tika’s integration in search engines, document processors, and content-analysis pipelines, this vulnerability poses a high-impact risk across enterprise environments.
22. Sharepoint Zero day (CVE-2025-53770)
CVE-2025-53770 is a critical remote code execution vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint Server that allows unauthenticated attackers to run arbitrary code due to unsafe deserialization of untrusted data. Despite previous patches, it remains exploitable with low complexity and is actively being used in the wild.
23. SAP Zero-Day CVE-2025-31324
CVE-2025-31324 is a critical RCE vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver AS Java 7.50’s Visual Composer Framework, allowing unauthenticated attackers to upload and execute arbitrary files. This flaw puts enterprise SAP systems at high risk of full compromise.
24. Microsoft SharePoint (CVE-2024-38094)
A deserialization vulnerability in Microsoft SharePoint allows attackers to execute remote code execution (RCE) attacks, which have been actively exploited. This vulnerability is listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, highlighting the urgency for patching. The rise of cyberattack statistics like these underscores how critical it is to address vulnerabilities swiftly.
Over 100,000 instances of Grafana, including nearly 19,000 in the U.S., are vulnerable to exploitation via SQL Expressions. Attackers can execute commands and access restricted files even with Viewer permissions.
26. CUPS Vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-47176, CVE-2024-47076)
Multiple vulnerabilities in the Common Unix Printing System (CUPS) have exposed 300,000 devices worldwide to remote code execution attacks. The severity of these cybersecurity breach statistics emphasizes the widespread impact of cyber crime statistics 2024, particularly in Linux environments like Debian, Red Hat, and macOS.
27. Ivanti Cloud Services Appliance OS Command Injection (CVE-2024-8190)
A vulnerability in Ivanti CSA versions 4.6 Patch 518 or earlier allows attackers with admin access to execute malicious commands remotely. Disclosed in September 2024, this flaw highlights the ongoing concern of cyber attackers targeting administrative privileges.
28. Apache OFBiz Pre-Authentication RCE (CVE-2024-38856)
This pre-authentication RCE vulnerability in Apache OFBiz allows unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code. The cyberattack stats show that vulnerabilities like these continue to be a major target, requiring organizations to upgrade to newer versions to mitigate risks.
29. GOAnywhere MFT Breach (CVE-2024-0204)
A critical vulnerability in Fortra’s GOAnywhere Managed File Transfer (MFT) software allowed attackers to create admin accounts, gaining full system control. All versions before 7.4.1 were affected, exposing organizations to data breaches.
30. ServiceNow Critical Vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-4879, CVE-2024-5217)
Threat actors exploited critical vulnerabilities in ServiceNow’s IT service management platform, leading to the exposure of over 105 ServiceNow databases. These flaws, with CVSS scores of 9.3 and 9.2, enabled data harvesting, with stolen records reportedly sold on forums for $5,000.
The CLOP ransomware gang exploited a vulnerability in MOVEit, a managed file transfer application, exposing 77 million records from over 2,600 organizations. Damages exceeded $12 billion, impacting organizations like the U.S. Department of Energy and Louisiana’s Office of Motor Vehicles.
32. Black Basta’s Privilege Escalation (CVE-2024-26169)
Exploited by the Black Basta ransomware group, this vulnerability enabled privilege escalation on unpatched systems. Despite being patched in March 2024, slow updates left systems exposed to attacks.
DDoS Attacks and Botnets Statistics for 2026
DDoS attacks and botnet-driven campaigns have surged, putting businesses at serious financial and reputational risk. With the growing scale and frequency of these threats, companies must strengthen defences to avoid severe impacts.
Here’s a look at the latest DDoS and bot attack statistics reshaping cybersecurity in 2026.
1. Global DDoS Volume – Across AppTrana-protected applications worldwide, more than 1.52 billion DDoS attacks were blocked in H1 2025, demonstrating that large-scale volumetric and low-and-slow DDoS campaigns remain one of the most persistent and high-frequency threats targeting internet-facing systems.[Indusface]
2. Despite the wide distribution of industries and architectures, 70% of all websites experienced at least one DDoS attack, highlighting that DDoS pressure is not limited to high-value verticals but affects the majority of applications regardless of size or geography. [Indusface]
3. Automated bot activity was even more widespread than DDoS, with 90% of monitored applications being targeted and a total of 64 million bot requests blocked, reflecting how credential stuffing, scraping, fake account creation, and L7 DDoS bots now form the default background noise for most modern applications. [Indusface]
4. API endpoints faced significantly heavier attack pressure, as API hosts suffered 388% more DDoS attacks per site than websites, showing that attackers increasingly aim at machine-to-machine interfaces that typically lack rate-based controls and require higher throughput. [Indusface]
5. When comparing traffic volume, APIs received 1403% more DDoS traffic than websites, reinforcing that APIs, not traditional web pages have become the preferred target for attackers attempting to overwhelm business-critical infrastructure.[Indusface]
6. Banking and Financial Services applications experienced a massive 518% increase in API DDoS attacks, showing that attackers aggressively target financial APIs to disrupt transactions, authentication flows, and critical backend connectivity.[Indusface]
7. Website DDoS attacks on BFS applications also rose sharply by 110%, indicating that both customer-facing portals and backend APIs in the financial sector faced sustained multi-vector DDoS pressure.[Indusface]
8. During the geopolitical event “Operation Sindoor,” BFS applications saw a sudden 172% spike in DDoS attacks within a single week, proving how real-world tensions translate into immediate cyber escalations against financial infrastructure.[Indusface]
9. Alongside the DDoS spike, overall attacks on BFS applications rose by 35% during the same week, confirming that DDoS campaigns were accompanied by coordinated vulnerability scanning, bot probing, and API exploitation attempts. [Indusface]
10. Botnets, particularly the Gorilla, the DDoS Botnet, have been responsible for over 300,000 cyberattacks, demonstrating the power of large-scale automated threats that can overwhelm targets, disrupt services, and evade traditional defence mechanisms.
11. The cost of DDoS attacks has drastically dropped, now as low as $5 per hour for renting botnet. This makes it easier for attackers to target businesses, contributing to the rising cyber-crime statistics.[G2]
12. The scale of DDoS attacks has increased, with some surpassing 71 million requests per second. This makes defending against such attacks even more challenging for companies. [Thehackernews]
13. SaaS and BFSI sectors are particularly vulnerable, with 10X more bot attacks in SaaS and twice as many attacks in BFSI. [Indusface]
14. DDoS attacks cost businesses up to $22,000 per minute in downtime, highlighting the severe financial impact of these cyber incidents. [Ponemon]
15. Online retailers and small businesses lose anywhere from $8,000 to $74,000 for each hour of downtime caused by a DDoS attack. This underscores the significant financial risk for businesses targeted by these campaigns.[G2]
16. The rise in DDoS attack statistics and botnet exploitation is set to continue. 58% of security leaders cite service disruption as a top challenge in managing DDoS attacks. [Indusface]
17. A notable increase in low-rate HTTP DDoS attacks driven by botnets was observed, highlighting the growing sophistication of these cyber campaigns in bypassing traditional defences. [Indusface]
18. Indusface’s State of Application Security 2024 Annual Reportreveals that 40% of these DDoS attacks were successfully blocked using static URI-based rate-limiting techniques. The remaining 60% were neutralized by AppTrana WAAP’s AI-driven behavioral models. [Indusface]
19. The average duration of a DDoS attack was 68 minutes across industries in 2024, but depending on the severity, attacks can last a day or longer, further extending business disruptions.[G2]
API Security Statistics 2026
As API security becomes a focal point in modern cybersecurity, the frequency and severity of breaches highlight critical vulnerabilities across industries. Recent cyberattack statistics underscore the urgency of securing APIs against evolving threats:
1. Global API Attack Growth – Across AppTrana-protected applications globally, API attacks increased by 104% year-over-year, indicating that attackers are shifting strongly toward machine-to-machine interfaces where authentication gaps, poor access controls, and complex integrations create broader exploitation opportunities. [Indusface]
2. India API Attack Growth – In India, API attacks surged even faster at 126% year-over-year, showing that Indian digital platforms, especially BFS, retail, and government-facing portals are experiencing a disproportionately higher rise in API-focused malicious traffic compared to the global average. [Indusface]
3. API Vulnerability Exploitation Spike – API vulnerability exploitation attempts skyrocketed by 13X (a 1304% increase), representing the sharpest growth across all attack vectors and proving that attackers now strongly prefer exploiting logic flaws, broken access controls, and misconfigured APIs over traditional web vulnerabilities. [Indusface]
4. API vs Website Attack Comparison – APIs were targeted far more aggressively overall, receiving 43% more total attacks than websites, showing that APIs have overtaken web pages as the primary entry point for both volumetric and exploit-based attacks. [Indusface]
5. Small and medium businesses recorded a 43% increase in API attacks, showing that API-driven abuse is no longer limited to large enterprises but is now pressuring smaller organizations with limited security teams. [Indusface]
6. SMB API hosts were hit extraordinarily harder, facing 741% more attacks than enterprise websites, which means SMB APIs are nearly eight times more likely to be targeted due to weaker rate-limiting, insufficient authentication layers, and minimal runtime API monitoring. [Indusface]
7. A buggy API on an insurance website exposed Office 365 passwords and over 50 million email records, demonstrating the catastrophic results of weak API protection.[Theregister]
8. A penetration testing revealed a vulnerable API in India that allowed access to over 650,000 sensitive messages, showcasing how easily attackers can compromise vast amounts of data.[Theregister]
9. Trello’s exposed API led to a breach impacting 15 million users, linking private email addresses to Trello accounts, posing significant risks for personal data exposure.[Bleepingcomputer]
10. Dell’s insecure API led to a breach impacting 49 million customer records, where attackers exploited the API to create fake accounts and exfiltrate data.[Bleepingcomputer]
11. 58% of companies identified data exfiltration as their top concern in API security, reflecting the growing threat of sensitive data leaks and breaches.[ai]
12. Over 50% of companies have delayed the release of new APIs due to concerns over security, indicating widespread awareness of the risks associated with insecure API endpoints.[Okoone]
13. 46% of organizations rely on penetration testing to assess vulnerabilities in APIs before deployment, with this practice becoming critical for pre-production API security.[ai]
AI Risks and Breach Costs to Watch in 2026
The AI Threat Outlook for 2026 reveals how adversarial use of AI, governance blind spots, and emerging attack techniques are reshaping breach impact and financial risk.[IBM]
1. Breaches where attackers used AI cost organizations USD 4.49 million, slightly higher than breaches involving traditional attack vectors.[IBM]
2. Sixteen percent of global data breaches involved attackers using AI, primarily through highly personalized phishing emails and deepfake impersonation attacks designed to bypass human judgment.[IBM]
3. Shadow AI emerged as a major cost amplifier, adding USD 200,000 to breach costs for organizations with high usage of unsanctioned AI tools.[IBM]
4. AI-driven and machine-learning insights reduced breach costs by USD 223,000, proving the value of predictive analytics and early anomaly detection.[IBM]
5. Sixty-three percent of organizations lacked any AI governance policy, exposing them to unmonitored model usage, shadow AI growth, and unreviewed AI deployment.[IBM]
6. A 2024/2025 peer-reviewed study on phishing shows that fully automated spear-phishing emails generated by large language models had a 54% click-through rate, matching phishing from human experts, far above a 12% baseline from generic spam.[arxiv]
7. The same study found that AI-generated phishing was about 350% more effective than random (control) phishing in yielding clicks, showing that AI substantially improves phishing success rate. .[arxiv]
8. A 2025 “State of Cybersecurity Resilience” report observed that only 36% of technology leaders say their security capabilities currently keep up with AI-driven threats, implying many organizations remain underprepared[accenture]
Cyber Threat Statistics and Business Risks 2026
Cyber Threats and Trends 2026
1. Breaches that took more than 200 days to detect and contain cost USD 5.01 million on average, significantly higher than breaches resolved within 200 days at USD 3.87 million. [IBM]
2. The overall breach lifecycle decreased to 241 days, reflecting a nine-year low in detection and containment time thanks to stronger automation and AI integration. .[IBM]
3. Every 39 seconds, a cybersecurity breach occurs, contributing to the 2,244 daily cyberattacks that threaten businesses and individuals.[ Clark School study]
4. 30,000 websites are compromised daily – Websites have become a prime target for cybercriminals, leading to data breaches, reputational damage, and financial losses.[Forbes]
5. In 2024, cybercrime costs are projected to reach $8 trillion globally, expected to almost triple by 2027, with losses predicted to hit $24 trillion.[USAID]
6. Similarly, cybersecurity ventures predicts that by 2025, cybercrime is estimated to cost $10.5 trillion, marking a continuous upward trajectory in losses from cyber incidents.[Business Standard]
7. Ransomware damages are projected to reach $265 billion annually by 2031, a sharp increase from $42 billion in 2024.[Sprinto]
8. The cost of recovering from a ransomware attack has risen to $2.73 million, nearly $1 million higher than in 2023, reflecting the growing financial strain of cyberattacks.[Sophos]
9. According to 2023 cybersecurity statistics, 83% of data breaches were caused by external parties.[Verizon]
10. Cyberattacks in India surged by 115% in Q2 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, indicating a significant rise in cyber threats in the region. [Indusface]
11. BFSI sectors (Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance) experience 2X more attacks per site than the global average. [Indusface]
12. Power and energy websites face four times more attacks than the average website, with an average of 1.9 million attacks per site. [Indusface]
13. On average, businesses spend $1 million on incident response.
Cyber Threats and Attack Vectors
14. Credential phishing was the most reported threat in 2023, with over 940,000 user reports. This underscores the importance of employee training and email security gateways to mitigate phishing risks.[Statista]
15. According to a Netwrix survey of 937 IT professionals worldwide, 82% of organizations identify credential stuffing as a significant threat. [ Netwrix]
16. Compromised credentials were the most common initial attack vector, responsible for 20% of breaches, with an average cost of $4.37 million per breach. [IBM]
17. Human error remains a major contributor to breaches, with users often falling for phishing emails within seconds. A recent report emphasizes this, reporting that 68% of breaches involve the human element.[Verizon]
18. In 2022, 12% of data breaches are caused by unsecured external-facing assets like servers and databases.[Blackkite]
19. In 2021, only 17% of small businesses implemented basic encryption for their data.[AdvisorSmith]
20. Alarmingly, 53% of small businesses reported having over 1,000 unencrypted sensitive folders, which exposes them to significant risk.[Security Magazine]
21. Additionally, 7 million unencrypted files are compromised daily, underscoring the ongoing vulnerabilities in data protection.[Veritas]
22. 60% of companies have 500+ passwords that never expire – Poor password management remains a significant vulnerability for organizations, exposing them to security risks.[Varonis]
23. Over 60% of financial services companies have 1,000+ sensitive files accessible to all employees – A massive internal security risk arises when sensitive files are accessible to all staff, increasing the likelihood of data breaches and insider threats. [Varonis]
24. 42% of organizations have experienced vulnerabilities leading to security incidents due to mobile devices and web applications, it’s clear that comprehensive security strategies must account for these high-risk areas.[purplesec]
Data Exposure and Security Breaches
25. Organizations using a DevSecOps approach saved approximately USD 227,000 per breach by shortening detection and improving remediation workflows.[IBM]
26. Nearly 1 billion emails were exposed within a year, impacting 1 in 5 internet users globally.[AAG]
27. Exploitations of public-facing applications accounted for 26% of incidents in 2023, highlighting the critical need for securing internet-accessible applications. [IBM Security X-Force].
28. Organizations without a zero-trust model experience breach costs $1 million higher than those that implement zero-trust measures [IBM].
29. Healthcare cybersecurity spending is estimated to reach $125 billion from 2020-2025 due to the increasing sophistication of attacks on patient data.[Cybercrime Magazine]
30. The Optus data breach, which occurred in September 2022, serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with poor data security. The breach, which compromised the personal details of 11 million customers, illustrates how even large enterprises can fall victim to cybersecurity breaches.
31. Only 69% of organizations use multi-factor authentication (MFA) for securing cloud environments, despite its proven effectiveness in enhancing security.[Netwrix]
32. The average cost of IoT attacks is $330,000 per incident, underscoring the importance of segmenting IoT devices from critical networks to contain potential breaches. [PSA Certified]
33. In 2024, the cost of cybercrime is set to skyrocket, with projections of $24 trillion in global losses by 2027. This highlights the escalating risks organizations face in the coming years.[Statista]
Key Data Breach Trends 2026
Rising Costs of Data Breaches
1. The global average cost of a data breach decreased to USD 4.44 million in 2025, marking the first decline in five years due to faster detection and containment driven by AI and automation.[IBM]
2. In contrast, the United States recorded an all-time high breach cost of USD 10.22 million, fuelled by stricter regulatory penalties and rising detection expenses.[IBM]
3. Healthcare remained the most expensive industry, with an average cost of USD 7.42 million, as attackers continue to target high-value patient identity data.[IBM]
4. The healthcare industry incurred the highest breach costs, averaging $9.77 million between 2022-2024. This is primarily due to the value of sensitive patient data, making healthcare organizations prime targets for cybercriminals. [IBM]
5. The Cam4 breach of 2020 exposed over 10 billion records, marking it as one of the largest data leak incidents to date. This reinforces the importance of secure database management and access controls. [Statista]
Cloud and Credential Risks in Breaches
As organizations increasingly migrate to the cloud, the risk associated with misconfigured cloud environments has grown:
6. 82% of breaches in 2024 are expected to involve cloud-based data, highlighting the need for robust cloud security practices. [IBM]
7. Cloud-based services are increasingly becoming prime targets for cybercriminals. 38% of SaaS applications are under attack, with cloud-based email servers also frequently targeted. [SentinelOne]
8. In fact, 80% of organizations have observed a rise in the frequency of cloud attacks, highlighting the growing vulnerability of cloud infrastructure in today’s digital landscape. [SentinelOne]
9. Additionally, 80% of breaches involved compromised or misused privileged credentials, further underscoring the importance of controlling access and ensuring secure credentials.[Verizon]
10. A report by IBM showed that 64% of Americans would hold companies accountable for personal data losses, rather than the attackers themselves, emphasizing the reputational and financial damage companies face following breaches.[Forbes]
11. 27% of businesses experienced a public cloud security incident in 2024. [SentinelOne]
12. 79% of organizations use more than one cloud provider, and this growing complexity is leading to more misconfigurations and security vulnerabilities.[SentinelOne]
13. Cloud misconfigurations account for 23% of security incidents, according to SentinelOne.
14. A 10% increase from the previous year, 27% of businesses have faced security breaches in their public cloud infrastructure. [Netgain Technologies]
15. On average, the price of a full exploit chain for Apple iOS is estimated at $2 million, underlining the growing financial incentives for cybercriminals targeting high-value platforms and users.[Purplesec]
Impact on SMEs and Downtime Costs
16. SMEs are particularly vulnerable, with 40% of SMEs experiencing over eight hours of downtime following a cyberattack. This downtime directly contributes to financial losses, making it crucial for SMEs to invest in proactive cybersecurity measures.[CISCO]
17. In 2023, cybercriminals stole more than $2 billion in cryptocurrency by exploiting security flaws in decentralized exchanges and wallets. This underscores the need for improved security in the rapidly growing cryptocurrency sector.[therecord]
Data Breaches by Industry
18. The ITRC’s mid-year 2025 report reveals 1,732 data breaches occurred in the first half of the year, marking an 11% rise from last year. This number already represents more than half (54.9%) of the total breaches recorded in 2024.
Between March 2022 and February 2024, the average costs of breaches by industry were as follows: [Statista]
19. Average breach cost: $9.77 million. High due to sensitive patient data and regulatory compliance.
20. Average breach cost: $6.08 million. Driven by financial data sensitivity & regulatory scrutiny.
21. Average breach cost: $2.55 million. Lower but impactful due to loss of public trust.
22. Average breach cost across all industries: $4.88 million. Reflects various industry risks and breach responses.
23. In 2022, identity fraud impacted 15.4 million U.S. adults, resulting in losses totaling $20 billion. This highlights the widespread impact of data breaches and the increasing need for organizations to protect sensitive consumer information.[Javelin Strategy & Research]
24. The cost of recovering from a ransomware attack is now averaging $2.73 million, a nearly $1 million jump from 2023. This significant increase reflects the growing sophistication of ransomware attacks and the heavy toll they take on organizations’ finances.[Sophos]
25. Gartner predicts global IT spending will grow by 8% in 2024, reaching $5.1 trillion, with 80% of CIOs planning to increase their cybersecurity budgets. This reflects the growing recognition of the need for enhanced cybersecurity measures in the face of rising threats.[Gartner]
Major Data Breaches and Exposed Information 2026
According to recent cyberattack statistics 2026, breaches involving personal data are becoming more common, with an increasing number of data breaches targeting sensitive consumer data.
26. A major security lapse in an AI-powered chatbot exposed the personal data of over 64 million McDonald’s job applicants. Two security researchers discovered the flaw after gaining access using the weak password “123456.”
27. AT&T Data Leak (2024): A breach of AT&T’s systems exposed personal information of around 73 million customers, including social security numbers, email addresses, and other sensitive data. This breach, which occurred on the dark web, underlines the critical need for robust data protection in telecommunications.
28. IMF Email Compromise (2024): The IMF faced a cyberattack in which hackers gained access to 11 email accounts, potentially exposing sensitive communications. While no broader breach occurred, this incident underscores the vulnerability of email systems to cyberattacks.
29. BBC Cloud Storage Breach (2024): The BBC reported a breach of its cloud storage service, which compromised personal data of over 25,000 employees, including information related to pension schemes. While financial details weren’t exposed, this breach highlights vulnerabilities in cloud-based storage and the sensitive nature of employee data.
30. Dell Data Breach (2024): A cyberattack against Dell compromised the data of 49 million customers. Attackers exploited an API vulnerability, using a brute-force method to extract data, exposing the risk of overlooked security flaws in large enterprise systems.
31. National Public Data Breach (2024): Jerico Pictures Inc.’s National Public Data service fell victim to a massive cyberattack. The hacker, “Fenice,” leaked an astonishing 2.9 billion records, including personal information such as names, addresses, and Social Security Numbers stored in plain text. The breach poses severe risks for identity theft and financial crimes, leaving Jerico Pictures Inc. exposed to potential legal battles and lawsuits.
32. FBCS Breach (2024): In February 2024, U.S.-based debt collection agency Financial Business and Consumer Solutions (FBCS) suffered a data breach, exposing sensitive information of over 4 million individuals. The breach, occurring between February 14 and 26, went undetected until February 26 and was disclosed publicly in April, revealing unauthorized access to confidential consumer data.
Rising Cyber Risks for SMBs 2026
Recent cyber security statistics show that SMBs are disproportionately targeted across multiple attack vectors from overwhelming DDoS campaigns to automated bot abuse resulting in prolonged outages and steep financial damage.
1. SMB Exposure to DDoS Attacks: Small and medium businesses experienced disproportionately higher DDoS activity, with 86% of all attacks on SMBs being DDoS-based, reflecting how attackers increasingly exploit the limited operational resilience of smaller organizations.[Indusface]
2. SMB vs Enterprise DDoS Gap: The disparity between SMBs and enterprises is stark, as SMB applications faced 1472% more DDoS attacks than enterprise applications, meaning SMBs were almost fifteen times more likely to experience service disruption due to resource exhaustion.[Indusface]
3. Bot attacks on SMBs surged to 6.79 million events, illustrating how automated abuse, especially credential stuffing, scraping, and checkout manipulation targets businesses with lower security investments and weaker fraud controls.[Indusface]
4. SMEs are particularly vulnerable, with 40% of SMEs experiencing over eight hours of downtime following a cyberattack. This downtime directly contributes to financial losses, making it crucial for SMEs to invest in proactive cybersecurity measures.[CISCO]
5. In 2023, cybercriminals stole more than $2 billion in cryptocurrency by exploiting security flaws in decentralized exchanges and wallets. This underscores the need for improved security in the rapidly growing cryptocurrency sector.[therecord]
DNS Security Statistics 2026
1. Organizations are facing 7.5 DNS attacks per year, with DNS-based attacks becoming more common. These attacks often target an organization’s DNS infrastructure, aiming to disrupt its online presence and services.[IDC Report]
2. DNS attacks lead to application outages in 82% of businesses and result in data theft in 29% of cases. This illustrates the devastating potential of DNS attacks, making DNS security a critical concern for businesses aiming to protect their digital assets.[G2]
3. DNS hijacking is a significant concern for 47% of organizations, leading to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. This further emphasizes the threat to critical services and infrastructure, as hijacking DNS settings can cause widespread service disruptions. [G2]
4. In 2021, a global survey of over 1,100 organizations revealed alarming statistics: [Heimdal Security]
5. 87% of organizations reported experiencing DNS attacks.
6. The average cost per attack globally was approximately $950,000, rising to $1 million for North American organizations.
7. The trend has only worsened. By Q1 2024, there were 1.5 million DNS DDoS attacks globally—a clear indication of the escalating threat landscape.
Supply Chain and Third-Party Risks 2025
1. Supply chain compromise was the most common cause of AI-related security incidents, at 30%, particularly involving vulnerable models, APIs, plug-ins, or third-party tools.[IBM]
2. Supply chain breaches added approximately USD 227,000 to the average cost, making them one of the most expensive incident types due to their complexity and extended detection times. .[IBM]
3. According to the 2025 DBIR report, 30% of breaches involved third-party vendors, twice the rate reported last year and were largely driven by vulnerability exploitation and business disruptions.
4. Supply chain security is increasingly critical, with 98% of businesses concerned about supply chain compromises. [Security Magazine]
5. Cyberattacks targeting the software supply chain are expected to cost the global economy $80.6 billion annually by 2026. [Juniper Research]
6. This category of attacks gained visibility following the SolarWinds breach in 2021, a significant incident attributed to a nation-state attack.
7. In fact, 62% of companies faced cybersecurity disruptions in their supply chains last year, according to the 2024 IT Risk and Compliance Benchmark Report.
8. In 2023, 61% of businesses experienced a breach involving a third-party vendor, a significant increase since 2021.[Prevalent]
9. Third-party incidents have far-reaching impacts: 84% cause operational disruptions, and 66% lead to financial losses, according to Gartner.
10. Resolving third-party breaches takes 12.8% more time and incurs 11.8% higher costs, with the breach lifecycle stretching to 307 days. [Prevalent]
11. Costing, on average, 40% more than internal breaches, third-party cyber incidents underscore the importance of strengthening risk management and performing ongoing evaluations of third-party systems. [Gartner]
12. Furthermore, survey respondents reported that third-party incidents also lead to reputational damage (59%).[Gartner]
13. 45% of organizations will face software supply chain attacks by 2025 – Third-party risks are on the rise, making external relationships a growing security concern. [ Gartner]
14. 54% of businesses do not properly vet third-party vendors, increasing the risk of cloud security breaches caused by third-party access.[zengrc]
Key Cybersecurity Stats on Malware & Ransomware 2025
1. 300,000 new pieces of malware created daily – Cybercriminals are continuously innovating and adapting their tactics, with new malware variants appearing each day.
2. 1.2 billion known types of malware – Including viruses, ransomware, and other malicious software, malware continues to be one of the most pervasive cybersecurity threats.[Stationx]
3. 6.06 billion malware attacks detected in 2023 – The volume of malware attacks worldwide reached record levels, reflecting the persistent and growing nature of malicious activity.[Statista]
4. Asia-Pacific region led in malware attacks in 2023 – Driven by a large number of digital platforms, the region saw the highest number of malware detections globally.[IDC]
5. The average cost of a ransomware attack in 2025, marking a 574% increase from $761,106 in 2019.[G2]
6. LockBit accounted for $91 million in ransomware payments Making it the most financially impactful ransomware group of 2025, while RansomHub was the most consistently active throughout the year.[G2]
7. Major botnet malware delivery infrastructures were taken down. The U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) seized over $24 million and disrupted key ransomware distribution networks. [G2]
8. 7% of organizations globally were victims of ransomware in 2023 – Ransomware continues to be one of the most disruptive and financially damaging forms of cyberattack.[Sprinto]
9. A ransomware attack costs an average of $4.54 million (excluding ransom), underscoring the need for proactive measures like endpoint security to mitigate financial strain. [IBM]
10. Ransomware attacks will strike every 2 seconds by 2031 – The growing frequency of ransomware attacks emphasizes the urgency for businesses to adopt layered defences like firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and ransomware-specific tools. [Cybercrime Magazine]
11. 54% of healthcare IT professionals believe their organizations are vulnerable to ransomware attacks – The healthcare sector remains highly susceptible to ransomware, highlighting the need for heightened cybersecurity vigilance. [Proofpoint]
12. 98% of mobile malware targets Android devices, a figure that underscores the importance of mobile security in today’s interconnected world.
Cyber Security Statistics for Compliance 2025
Strategic Focus and Leadership in Compliance
1. 42% of legal and compliance leaders plan to strengthen their personal impact on company strategy, signalling a shift toward more proactive compliance management. [Gartner for Legal, Risk & Compliance Leaders, July 2025 Survey]
2. 40% of leaders are prioritizing improvements in third-party risk management, addressing critical vulnerabilities. [Gartner]
3. 39% of leaders aim to ensure their compliance programs can keep pace with fast-moving regulatory requirements, highlighting the growing challenge of evolving regulations. [Gartner]
4. 70% of corporate risk and compliance professionals now focus on a strategic, outcome-driven model, moving beyond the traditional “check-the-box” approach. (Thomson Reuters Risk & Compliance Survey Report, 2023)
Costs and Consequences of Noncompliance
5. As of March 2025, regulatory authorities under General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) had issued a total of 2,245 fines, cumulatively amounting to € 5.65 billion, showing that noncompliance is leading to very substantial aggregate financial penalties.
6. The average fine per GDPR enforcement action (based on that 2025 data) is approximately € 2.36 million, highlighting that even mid-scale violations (not just headline-making ones) carry serious financial risk
7. Under GDPR, the sanctioned maximum fine for serious violations can be as high as € 20 million or 4% of a company’s global annual turnover (whichever is higher), making worst-case noncompliance potentially catastrophic for large organizations.
8. PCI DSS (payment-card data compliance): non-compliance can result in fines or penalties from acquiring banks/card networks , typically USD 5,000–100,000 per month until compliance is restored.
9. HIPAA (in the U.S., for healthcare data): fines vary by severity; for organizations mishandling protected health information (PHI), penalties may range from ≈ USD 141 up to USD 2.13 million depending on violation type and willfulness
10. DPDP Act allows the Data Protection Board of India to levy penalties up to ₹250 crore (₹2.5 billion) per instance of non-compliance, making it one of the highest penalty ceilings among Asian data-protection laws.
11. The average cost of a data breach rises by $220,000 when noncompliance with regulations is a factor, significantly increasing the financial impact. [IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, 2023]
12. The average breach cost for organizations with high noncompliance is $5.05 million, a 12.6% increase from the earlier average of $4.49 million. [IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, 2023]
13. The average compliance cost for organizations globally is $5.47 million, with financial services facing the highest average costs of $30.9 million. [IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, 2023]
14. In 2018, noncompliance led to an average business disruption cost of $5.1 million, showing the wide-reaching effects of regulatory failures.[corporatecomplianceinsights]
15. The Intercontinental Exchange was fined $10 million in 2024 for not meeting data breach reporting requirements, illustrating the importance of adhering to data protection regulations.
The Role of Technology in Compliance Management
16. Only 69% of businesses use compliance technology to streamline their programs, reducing manual effort and increasing accuracy.[safetica]
17. Companies that enable compliance technology save an average of $1.45 million in compliance costs, highlighting the financial benefits of leveraging tech tools.
18. Regular compliance audits save businesses an average of $2.86 million, emphasizing the importance of proactive compliance monitoring.
19. Despite the availability of advanced tools, 14% of businesses still rely on spreadsheets to manage IT compliance, illustrating the need for modernization.
Data Privacy and Regulatory Fines
20. The largest GDPR fine to date was €1.2 billion ($1.3 billion USD) for Meta in May 2023, showing the serious financial repercussions of noncompliance. [CNBC]
21. €1.1 billion in GDPR fines were issued between January 2021 and January 2022, reflecting growing regulatory enforcement. [DLA Piper]
22. Since GDPR enforcement began in May 2018, non-compliance with general data processing principles has accounted for the largest share of fines. By September 2024, these violations have resulted in fines exceeding €2.4 billion.[Statista]
23. Meanwhile, the FTC took action against 20 companies between August 2023 and August 2024 for data privacy and security breaches, including a recent case against Verkada for mishandling personal data and violating the CAN-SPAM Act. These actions highlight the increasing focus on data protection compliance.
24. 94% of customers avoid brands that mishandle their personal data, making data privacy a key factor in maintaining customer loyalty.[CISCO]
25. 82% of businesses consider ISO certifications like ISO 27001 and ISO 27701 critical for securing client trust and reinforcing their commitment to compliance. [Cisco]
Legal and Consumer Privacy Protection
26. The CCPA protects $12 billion in personal information annually, ensuring both compliance and consumer trust.
27. 9% of businesses use compliance solutions to adhere to data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, ensuring they stay within legal boundaries.
28. 7% of companies have updated their privacy policies to meet GDPR and other regulations, with 80% making multiple updates over the past year.[Legaljobs]
Key Cybersecurity Adoption Rates 2025
1. Security system complexity increased breach costs by USD 207,000, as fragmented and poorly integrated systems hinder quicker response.[IBM]
2. Zero Trust approach, which assumes no trust by default, has proven effective, saving $1.76 million per breach on average.
3. In 2023, 47% of organizations began leveraging Artificial Intelligence (AI) for cyber risk detection and mitigation, demonstrating AI’s increasing role in safeguarding digital infrastructure.[PWC]
4. As more businesses adopt multi-cloud strategies, Cloud Web Application and API Protection (WAAP) services are rapidly replacing traditional WAAP tools. By 2024, 70% of organizations are expected to rely on these services to protect their production environments from cyber attacks.[Gartner]
5. By 2026, over 40% of organizations with consumer-facing applications will rely on specialized providers for additional anomaly detection technology, up from less than 10% in 2022.[Gartner]
In conclusion, the cybersecurity landscape in 2024 shows a significant rise in attacks, particularly DDoS and exploitation of open vulnerabilities. As you face heightened risks, it’s crucial to prioritize strong security measures, including proactive vulnerability management and advanced threat detection. By staying informed about these cyber trends and investing in the right security solutions, you can better protect your organization from evolving cyber threats and safeguard your digital assets.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.

 December 12, 2025
December 12, 2025




