All You Need To Know About DROWN Attack
Identified as a low cost attack, DROWN allows hackers to decrypt browser-server communication in hours to attack servers or/and users. Shockingly, this newly found vulnerability works even on TLS servers, and affects yahoo.com, alibaba.com, buzzfeed.com, flickr.com, and cnbc.com to name a few.
DROWN vulnerability and affected website list was publicly disclosed on March 1, 2016, still many websites have failed to secure their primary and subdomains. Roughly, 11 million email servers and websites were vulnerable to this attack on March 1.
What Exactly is DROWN?
Decrypting RSA with Obsolete and Weakened eNcryption (DROWN) is a vulnerability discovered in OpenSSL that allows attackers to decrypt secure HTTPS browser to server communication.
Researchers from Münster University of Applied Sciences, Department of Electrical Engineering, Horst Görtz Institute for IT security, Tel Aviv University, Ruhr University Bochum, Hashcat Project, University of Pennsylvania, University of Michigan Google/OpenSSL, and Two Sigma/OpenSSL uncovered the vulnerability.
Notably, DROWN attack targets SSLv2, an old and deprecated encryption protocol. SSLv2 had a reputation of being badly insecure even in the 90s and was soon discarded to secure user-to-server communications. Even though most modern-day web servers and websites do not use the TLS encryption protocol, many servers can still support SSLv2 due to default settings and misconfiguration.
What Are The Exploitation Risks?
Hijacking the user to browser communication means that attackers can get their hands on whatever is being sent. This includes documents, instant messages, emails, credit card numbers, passwords, usernames, and other sensitive information.
However, the exploitation risks are not limited to stealing sensitive information. Attackers can use it to reach the website server or impersonate secure website or messages to users.
Are You Vulnerable to DROWN Attacks?
If your server allows SSLv2 connections and is not protected by web application firewall, it is vulnerable to DROWN attacks. While administrators are certain of discarding support for SSLv2, they might be unaware of default setting issues and other misconfigurations.
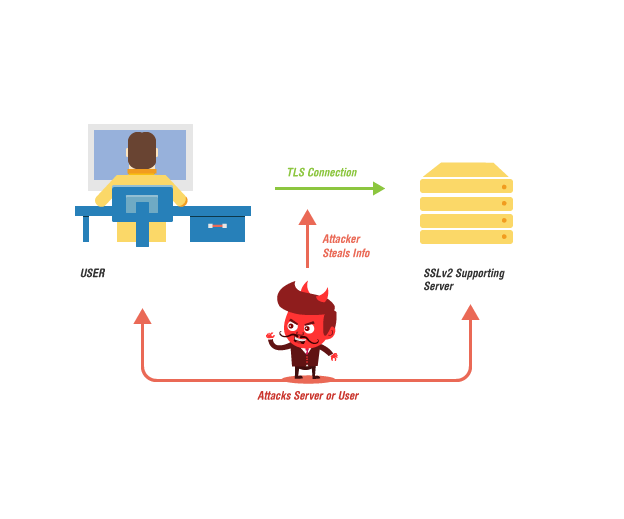
Please note that hackers can also exploit DROWN even if you allow private keys on any other server that might support SSLv2. This is extremely critical for email service providers, who often use the same cert on their email and web servers.
AppTrana will also flag servers that are vulnerable to the DROWN attack.
How to Prevent DROWN Attacks?
Ideally, server operators and administrators should look for misconfigurations that allow SSLv2 support and terminate it immediately. However, it is a complicated process and might take days to find the configuration and default setting error. OpenSSL recommends upgrading to the most recent OpenSSL version.
As informed to our customers, AppTrana Web Application Firewall (WAF) services are not impacted since SSLv2 is not enabled on our WAF solution. There is no way a man in the middle can access your RSA keys.
Find out more about Indusface Web Application Firewall and how it prevents zero-day vulnerability attacks here.
Stay tuned for more relevant and interesting security articles. Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn.


 March 22, 2016
March 22, 2016



