OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities in 2021: How to Mitigate Them?
The OWASP Top 10 is a research-based document that raises awareness among developers, organizations, and security professionals on the most critical security risks facing web applications. The latest is the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities 2021, released in September 2021 after a 4-year gap.
In this article, the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities 2021 are explained in detail, along with ways to mitigate each.
OWASP Top 10 Vulnerabilities 2021 & Mitigating Them
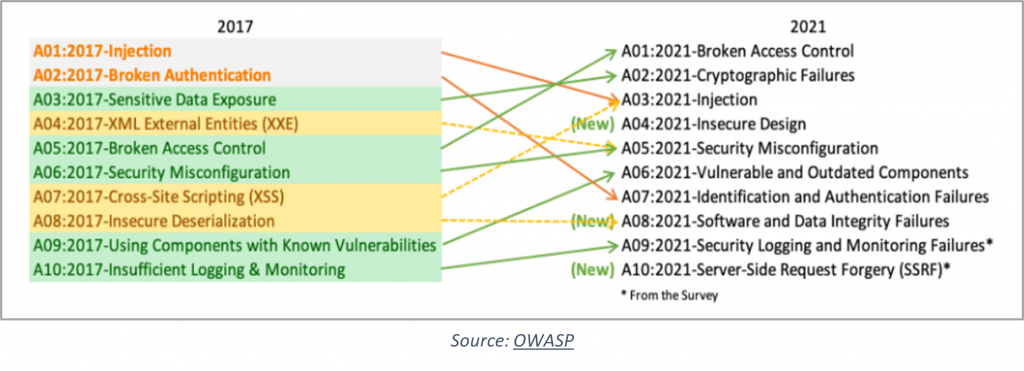
Source: OWASP
A01:2021-Broken Access Control
Broken access control vulnerabilities enable attackers to gain access to user accounts, admin panels, databases, servers, sensitive information, business-critical apps, etc., and let unauthorized users perform privileged functions such as modification or destruction. Broken Access Control has moved to the top of OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities 2021 since 94% of applications were found to have this vulnerability.
Mitigation:
- Adopt a least-privileged approach
- Build strong access controls using role-based authentication mechanisms
- Except for public resources, deny default access to functionalities
- Maintain lean servers by shutting down unnecessary services, deleting inactive and unnecessary accounts
- In case of multiple access points, disable ones that aren’t necessary
- Rate limit API and controller access
- Sensitive data must not be stored in the root
- Server directory listing must be disabled
A02:2021-Cryptographic Failures
Cryptographic Failures, previously known as “Sensitive Data Exposure,” ranks second in the OWASP Top 10 for 2021. This category highlights vulnerabilities that result from improper encryption or a complete lack of encryption, which can expose sensitive data to unauthorized parties.
As applications handle increasing amounts of personal, financial, and other confidential data, robust cryptography is essential for ensuring data privacy and integrity. Cryptographic failures can stem from weak algorithms, inadequate key management, or unencrypted sensitive data in transit or at rest. Addressing these weaknesses is crucial for preventing data breaches and protecting user privacy.
Mitigation:
- Encrypt all data at rest using secure and robust encryption algorithms, keys, and protocols
- Encrypt all data in transit using the latest, secure protocols like TLS
- Identify and apply strong security controls on all sensitive data
- Don’t collect and store sensitive data unless absolutely necessary
- Don’t cache sensitive data or on data-collecting forms
- Disable autocomplete on forms
- Minimize the attack surface
- Store passwords using robust, adaptive, and proven hashing functions
A03:2021-Injection
Injection vulnerabilities, now ranked third in the OWASP Top 10 for 2021, remain one of the most common and dangerous web application security risks. These occur when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query. Attackers can exploit injection flaws, like SQL, NoSQL, and command injection, to execute malicious commands, manipulate databases, or gain unauthorized access to systems.
Often caused by insufficient input validation or improper sanitization, injection attacks can lead to data breaches, data loss, or even full system compromise. Preventing injection vulnerabilities requires strong input validation, parameterized queries, and secure coding practices.
Mitigation:
- Server-side input validation is a must
- Use safe APIs to avoid interpreters completely
- Use intrusion detection systems to spot suspicious behavior
- Use parameterized queries
- Use LIMIT and other SQL controls within queries, preventing mass disclosure of records
- Avoid special characters
A04:2021-Insecure Design
Entering the list at #4, this new entrant in the OWASP Top 10 web application vulnerabilities 2021 list focuses on the risks associated with design flaws that lead to poor security controls. It reflects the industry’s growing focus on creating secure-by-design apps.
Mitigation:
- Integrate security right into the SDLC stages and leverage robust security practices from the early stages
- Establish a library of secure design patterns, components, frameworks, etc. that are ready and safe to use for new applications
- Use threat modeling for designing critical features like access controls, authentication, business logic, key flows, etc.
- Include security language, concerns, and controls in all user stories
- Based on exposure and protection needs, divide apps into different tiers and find use and misuse cases for each tier
- Each level of the app should include plausibility tests
A05:2021-Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration has risen to the fifth spot in the OWASP Top 10 for 2021, reflecting its widespread presence across web applications. This vulnerability occurs when an application or server lacks proper security hardening, often due to misconfigured settings, excessive permissions, or poor maintenance practices.
In fact, nearly 90% of applications are reported to have some form of security misconfiguration, highlighting its prevalence and the risks it poses to application security.
Mitigation:
- Harden app security using fast, easy to deploy processes
- Use preconfigured templates (with different credentials) to configure development, QA, and production identically
- Maintain a library of securely configured container images
- Remove unused features and services and deploy an application with minimal setup
- Regularly update and patch configurations
- Use automated workflows to verify secure configurations and detect misconfigurations in any environment. Remediate identified issues instantly.
A06:2021-Vulnerable and Outdated Components
This vulnerability arises from unsupported and outdated components, software, libraries, frameworks, etc. Building or using applications without the latest/ updated versions of components leaves them open to attacks.
Mitigation:
- Maintain an updated inventory of all components used in the application with their versions
- Continuously scan components, libraries, etc. and their dependencies for vulnerabilities
- Keep all components updated. If patches aren’t immediately available, apply virtual patches
- Remove unused, legacy, and outdated components, features, and dependencies from apps
- Use components, software, etc. from official and trustworthy sources
A07:2021-Identification and Authentication Failures
Incorrect execution of functions related to user authentication and session management allows users to compromise security keys, passwords, etc. and exploit permissions, assume identities, and so on, permanently or temporarily.
Mitigation:
- Multi-factor authentication is a must
- Don’t use default credentials, especially for admin privileges
- Implement a strong password policy
- Deploy a secure sessions manager that generated time-limited session IDs
- Monitor failed login attempts and set limits and delays on the same
- Strengthen registration, credential recovery, and other authentication-related processes
A08:2021-Software and Data Integrity Failures
Entering the OWASP Top 10 2021 at #8, this vulnerability highlights the need to verify the integrity of software updates, critical data, and CI/CD pipelines. Given the rise in supply chain attacks and their massive impact, this inclusion has been made. A8: 2017 – Insecure Deserialization vulnerability is now part of this larger category.
Mitigation:
- Ensure the legitimacy of software/ data/ programs and its source through digital signature or similar measures
- Ensure integrity of CI/CD pipeline through strong access controls, proper configuration, and adequate segregation
- Continuously review code and configurations for modifications
- Ensure that libraries and dependencies use trusted repositories. You can host an internal, approved, and known repository if your risk profile is higher
- Unencrypted serialized data must not be delivered to untrustworthy clients, so incorporate integrity checks
A09:2021-Security Logging and Monitoring Failures
This OWASP Top 10 vulnerability 2021 concerns the application’s weaknesses in detecting and responding to security risks. Given that the time taken to attack detection is 197 days on average, attackers have a long enough window to do their bidding.
Mitigation:
- Use readily available logging and audit software that helps in instant detection of suspicious activities
- Ensure the logs are contextual and available in compatible formats for in-depth forensic analysis
- Enforce security controls that help prevent the tampering of log data
A10:2021-Server-Side Request Forgery
In the OWASP Top 10 for 2021, Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF) holds the 10th position. SSRF vulnerabilities occur when an application fetches resources on behalf of a user, allowing attackers to manipulate those requests to access or modify resources on a server that they shouldn’t have access to. Even firewall/ VPN-protected servers are prone to these vulnerabilities if unvalidated user inputs are accepted.
Example of an SSRF Attack
Imagine an application feature that allows users to enter URLs to fetch images or other resources. Without restrictions, an attacker could input internal URLs, such as http://localhost/admin or http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data/ (the AWS metadata service endpoint). Through this SSRF vulnerability, the attacker could access sensitive administrative panels or retrieve metadata information, including access tokens for cloud resources.
Mitigation:
- Enforce input validation and sanitization on user inputs
- Remote resource access functionalities, if any, must be isolated in a separate environment
- Block unwanted incoming traffic using default-deny firewall policies
- Ensure clients don’t receive raw server responses
- Build a positive allowlist for ports, destinations, and URL schemes
- Disallow unsafe or external HTTP redirections
The Way Forward
Indusface’s next-gen, intelligent WAF provides effective protection against the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities 2021 and other security threats.
Found this article interesting? Follow Indusface on Facebook, Twitter, and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.


 November 13, 2024
November 13, 2024






