What is a VoIP Flood Attack?
A VoIP flood attack is a type of Denial of Service (DoS) attack that targets VoIP systems where an attacker sends an overwhelming amount of fake traffic to the VoIP server, making it difficult or impossible for legitimate calls to go through. This results in degraded service, dropped calls, or even a complete system shutdown.
What is VoIP?
VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) is a technology that allows you to make voice, and video calls over the internet instead of using traditional phone lines. It converts your voice into digital data, sends it over the internet, and then converts it back to sound at the other end. Popular VoIP services include Skype, Zoom, and business phone systems.
How Does a VoIP Flood Attack Happen?
VoIP systems rely on various protocols to function, primarily Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) for managing calls and Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) for transmitting voice data. An attacker exploits these protocols to flood the system with fake traffic, causing it to become overloaded.
Here’s how the attack occurs:
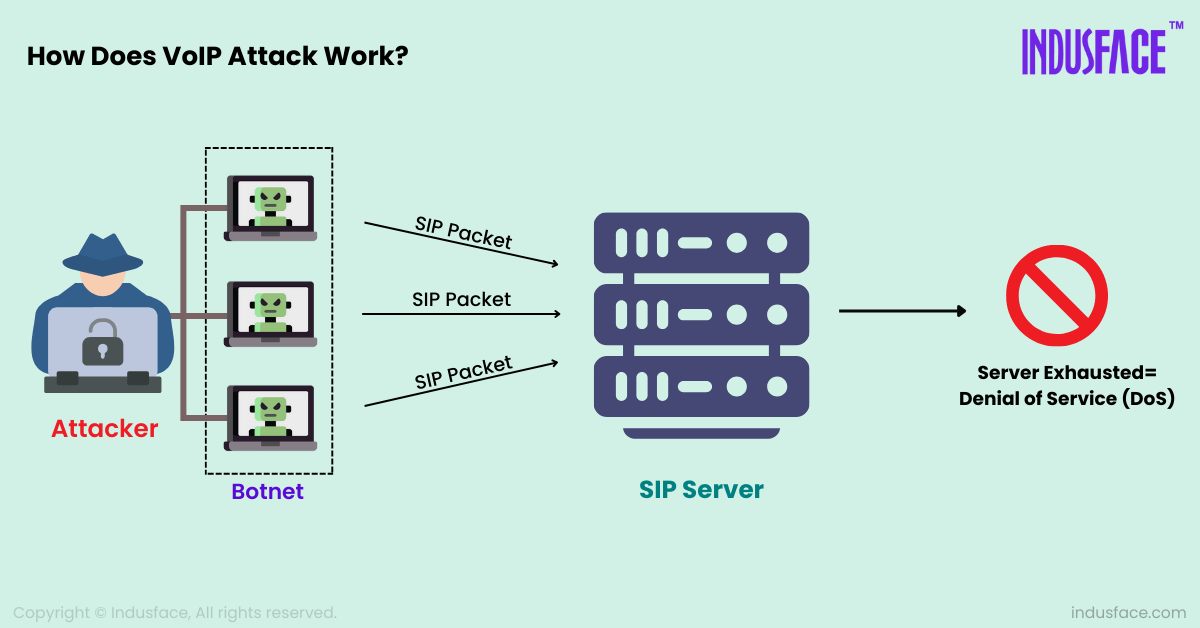
Launching the Attack: Attackers typically use botnets (networks of compromised computers) to generate a massive number of fake SIP requests. These requests could be fake call invitations, registrations, or even session terminations.
Overloading the Server: The VoIP server must process every incoming request, whether it is real or fake. During an attack, the server becomes overwhelmed by the sheer volume of fake traffic, using up CPU, memory, and network resources leading to resource exhaustion.
Disrupting the Service: As the server struggles to handle the traffic, legitimate calls get delayed, dropped, or cannot connect at all. In some cases, the entire VoIP service may crash, leading to complete disruption.
How to Detect a VoIP Flood Attack?
Here are some signs that your system might be under attack:
Increased Call Drop Rates: If you notice a significant rise in dropped or failed calls, it could be a sign of a VoIP flood attack overwhelming your system.
High Server Resource Usage: During an attack, you might observe your VoIP server using a lot of CPU or memory resources. If your server is constantly near its resource limits, it may be struggling to process a flood of SIP request.
Abnormal Call Behaviour: Look for strange patterns like a high number of short-duration calls, failed call setups, or excessive registration requests from unknown sources.
How to Prevent VoIP Flood Attacks?
Here are some effective ways to protect your VoIP system:
Rate Limiting – Implement rate limiting on your VoIP server to control the number of SIP requests that can be processed at any given time.
Authentication Mechanisms – Ensure that your VoIP system has robust authentication protocols in place, like TLS (Transport Layer Security) or IP-based authentication. This helps prevent unauthorized devices from sending SIP requests to your server.
Load Balancing – Distribute incoming VoIP traffic across multiple servers using load balancing. This decreases the chances of any one server becoming overwhelmed by a flood of requests.
Update and Patch Regularly – Regularly update your VoIP software and hardware to ensure you are secured against known vulnerabilities. Attackers often exploit outdated systems, so patching your systems is essential.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) – It detects abnormal patterns, such as excessive SIP or RTP requests and blocks or throttles the malicious traffic before it can impact the VoIP system, ensuring continued service availability while minimizing disruptions.
DDoS Protection Solution – DDoS protection solutions use traffic analysis, pattern recognition, and machine learning to differentiate legitimate VoIP traffic from attack traffic, such as a flood of SIP or RTP requests. When a VoIP flood is detected, the anti-DDoS tools automatically filter out the malicious traffic, allowing only legitimate requests to reach the server. Additionally, these tools can absorb and disperse the attack traffic through global networks of scrubbing centers, ensuring minimal disruption to VoIP services while maintaining call quality and availability.


 AppTrana WAAP Platform
AppTrana WAAP Platform


