From the helpful chatbots guiding us through customer service inquiries to the automated web crawlers indexing the vast expanse of the internet, bots have become an integral part of our digital landscape.
But what exactly is a bot, and how does it shape our online interactions?
According to many reports, bot traffic is almost 50% of internet traffic. Two-thirds of that is bad bot traffic.
In this blog, we’ll cover the definition of bots, how they evolved, the types of bots and finally how they impact us in our day to day lives.
What is a Bot?
A bot is a software application or program that performs automated tasks. Bots have evolved since the mid-1960s from early chatbots like ELIZA.
Initially used for web indexing, they now serve diverse roles in social media and customer service, harnessing AI and NLP advancements.
Bots can be designed to interact with users, perform specific functions, or simulate human behaviour.
Types of Bots
At a high level, there are two kinds of bots, good bots and bad bots (malicious bots).
Good Bots
Good bots are designed to perform useful or beneficial tasks that enhance user experiences, streamline processes, or provide valuable services. They aim to assist users, automate repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and deliver relevant information or functionality.
Real-World Applications and Examples of Good Bots
Chatbots
These bots engage in conversations with users, typically through text or voice interfaces. These range from commercial offerings on Intercom, Freshworks and the likes to consumer chat bots such as Alexa or Siri.
Web Crawlers
Bots that systematically browse the web to index or scrape content. Search engine bots such as Googlebot and Bingbot, web scrapers such as Octoparse and Import.io, pricing scraper bots such as PriceGrabber or PriceRunner and Dynamic Application Security Tools such as Indusface and Qualys are examples of web crawlers.
Trading bots
Automated programs that execute trades on financial markets based on predefined algorithms, often used in algorithmic trading and high-frequency trading.
They aim to capitalize on market inefficiencies and fluctuations to generate profits for traders and investors. In addition to crypto trading bots like Gunbot and HaasBot, there are also trading bots tailored for traditional financial markets, such as stocks and forex.
Monitoring bots
Bots used to monitor websites, servers, and networks for performance, and downtime. Monitoring bots play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and stability of digital services by alerting administrators to problems and facilitating timely troubleshooting and maintenance. Pingdom, Nagios, site24x7 are some examples of monitoring bots.
Utility bots
Utility bots provide a wide range of services on websites and messaging platforms, serving as virtual assistants for users’ everyday needs. By leveraging APIs and web scraping techniques to access external data sources and deliver relevant information and services to users in a convenient and accessible manner.
Bots used in various websites for services such as translation, weather updates and news fall in this category.
Malicious Bots
Bad bots are designed to perform malicious, harmful, or undesirable tasks that disrupt systems, exploit vulnerabilities, or deceive users. They aim to commit fraud, spread malware, steal sensitive information, manipulate data, or sabotage online operations.
Good bots operate with explicit authorization and adhere to legal and ethical standards, while bad bots operate without authorization and violate terms of service and security protocols.
Examples of Malicious Bots
Bots designed to carry out malicious activities, such as DDoS attacks, phishing, account takeover, data scraping, and spreading malware. Companies usually employ sophisticated bot management platforms to block these.
Other bots in this category include social media bots, which are typically used to spam, spread misinformation and boost engagement artificially, and Gaming bots, which are used in online gaming to automate gameplay, cheat, or manipulate in-game economies.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bots
Advantages
Efficiency: Bots can perform tasks faster and more consistently than humans, leading to increased productivity and efficiency in various domains.
24/7 Availability: Bots can operate around the clock without the need for breaks or downtime, providing continuous support and services to users.
Scalability: Bots can handle a large volume of requests simultaneously, making them well-suited for tasks that require scalability, such as customer support and data processing.
Cost Savings: Bots can reduce operational costs by automating repetitive tasks and minimizing the need for human intervention, especially in areas like customer service and data entry.
Accuracy: Bots can perform tasks with a high level of accuracy and consistency, minimizing errors and improving the quality of outcomes.
Disadvantages
Overall, while bots offer numerous benefits in terms of efficiency, scalability, and cost savings, they also pose challenges such as:
Lack of Human Touch: Bots may lack the empathy and understanding that human interactions provide, leading to less satisfying user experiences in certain situations, such as customer service.
Complexity: Developing and maintaining bots can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring expertise in programming, artificial intelligence, and natural language processing.
Dependency on Technology: Bots are reliant on technology infrastructure and may be susceptible to technical issues, such as system failures or software bugs, which can disrupt operations.
Privacy and Security Concerns: Bots may raise privacy and security concerns, especially when handling sensitive data or interacting with users in sensitive contexts. Unauthorized access or misuse of bots can lead to data breaches and other security incidents.
Limited Contextual Understanding: Bots may struggle to understand complex or ambiguous language, leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations in conversations with users. They may also lack the ability to understand non-verbal cues and context, which can impact their effectiveness in certain scenarios.
How do Bots Work?
Bots work by executing automated tasks based on predefined instructions or algorithms.
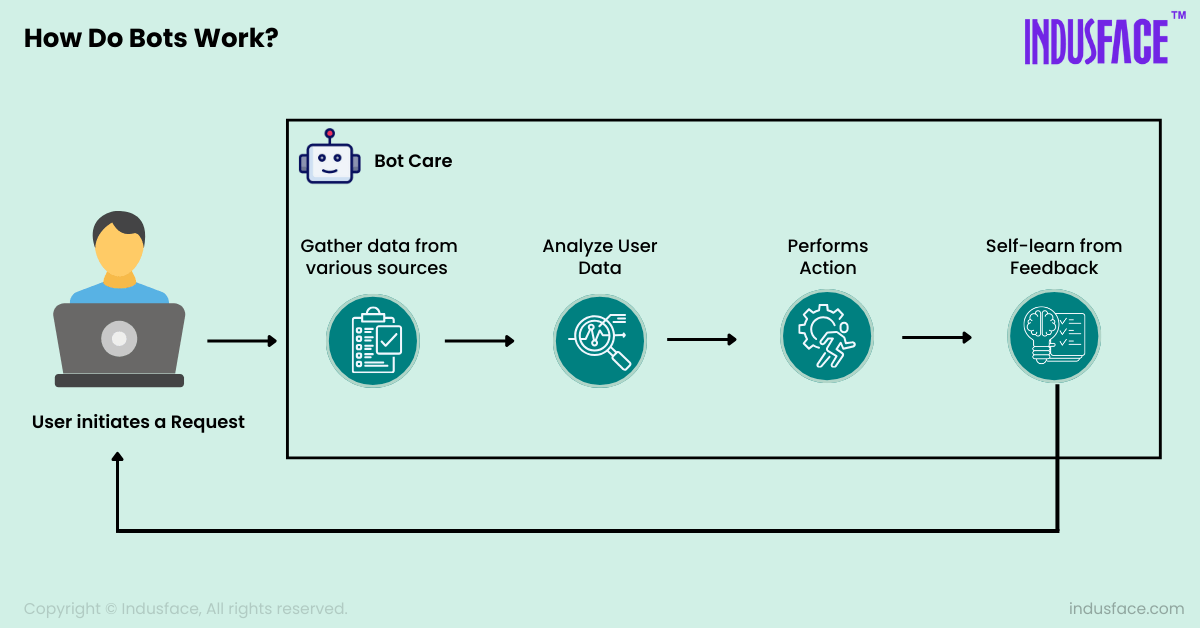
Here’s a simplified explanation of how bots typically work:
1. Initialization: The first step is initialization either by a user or an automated system.
2. Data Retrieval: Once initialized, bots gather data from various sources, such as websites, APIs, databases, or messaging platforms.
3. Processing: Once the data is retrieved, the bots analyse the data, extract relevant information, make decisions, and generate responses based on predefined rules or machine learning models.
4. Action: Depending on the purpose, the bot may take various actions based on the processed data. For example, a chatbot may respond to user inquiries and a web crawler may index web pages for search engine results.
5. Feedback and Learning: With the advancements in AI/ML, bots now use machine learning to automatically improve themselves over time by analysing feedback received over time. The feedback can come from user interactions, system metrics, or external data sources.
While this is one complete cycle, most bots repeat steps 1-5 in an endless loop or until a specified end goal has been met.
How to Detect and Block Malicious Bots?
Detecting bots can be challenging due to their diverse capabilities, evolving tactics, and ability to mimic human behaviour.
However, when combined with measures such as honeypots and CAPTCHA challenges, behavioral analysis of the site traffic works best in detecting and blocking malicious bot traffic.
It is good to benchmark all traffic against the usual traffic pattern on parameters. Here is a sample list of questions on behavioural analysis:
1. How many requests do I receive from a single IP in a specific time period?
2. Is the overall site traffic usual or in orders of magnitude higher than usual?
3. Is the IP listed in any malicious databases such as Spamhaus?
4. For a request from this IP, what is the bounce rate like? Is it typical behaviour or is there an anomaly?
5. Do the requests from a specific user agent have supporting headers?
6. Do I receive so much traffic from this geographic region at this time?
Rate limiting helps stop bad bots by limiting how many requests they can make. By analyzing how traffic behaves, determine the optimal rate limits for your protection.
For websites that see the requests in large volume, investing in advanced bot management solutions with machine learning will help analyze anomalies in real-time and take mitigation measures promptly.
Check out top 13 Bot Management Software in the Market.
How do Bot Management Solutions Help?
According to many studies, bad bots contribute to almost 30% of internet traffic and they can lead to data breaches, loss of customer trust, compliance fines and many more unfavourable outcomes for businesses.
It is therefore prudent to invest in bot management solutions to filter out bad bots and protect applications from a variety of attacks including DDoS, scalping, scraping and so on.
About AppTrana’s Bot Management Capabilities
AppTrana WAAP is an AI-powered, fully managed bot management solution. You get protection against account take over, card cracking, scalping and other attacks from day zero.
Machine learning for behavioural analysis and anomaly scoring combined with extensive false positive testing by the managed services team ensures that you filter out only bad bots.
The managed services team helps with 24×7 anomaly monitoring and workflow-based security policies to block advanced business logic vulnerability attacks.
In conclusion, understanding bots and their various types is essential in today’s digital age. While good bots can greatly enhance user experience and efficiency, malicious bots pose significant risks. Investing in robust bot management solutions is crucial to safeguarding your applications and data.
Start a 14-day free trial today to expereince the bot management capabilities on AppTrana WAAP.


